In the early days of search, people refined their queries one step at a time. If the first result did not match their need, they tweaked the wording or added a keyword and tried again. That method, which we call “query stacking,” was simple and linear.
It is easy to follow and to track. Each query is logged separately, so you can see precisely how people moved from one term to the next. Today, Google is rolling out an AI-powered layer that changes the game.
With Query Fan-Out, a single prompt can trigger multiple internal queries simultaneously. This approach aims to address every common angle in a single response. It can save users time, but it also raises new challenges for those who study search behavior and create content.
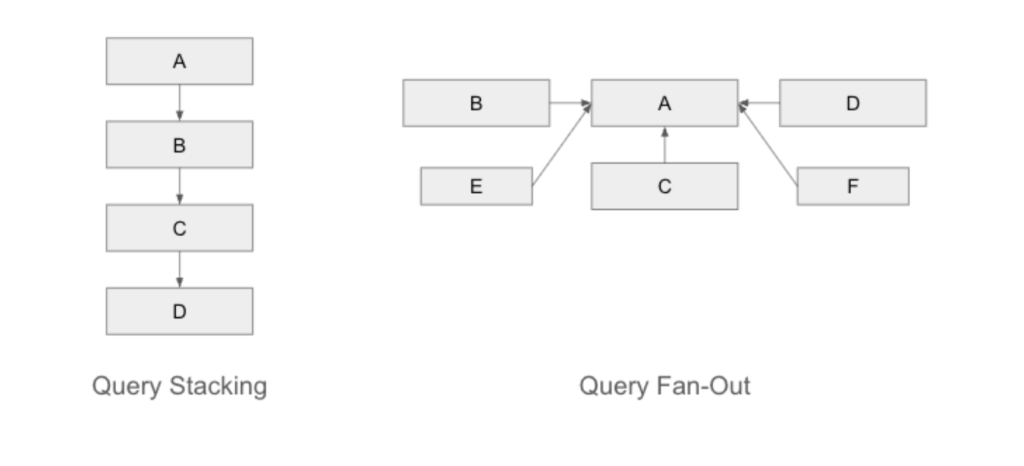
Linear query stacking
Query stacking refers to the traditional method of refining searches incrementally, with each subsequent query building upon the previous one.
For example, someone might start with “best summer destinations,” then narrow it to “best summer destinations in Europe,” and finally to “best summer destinations in Europe for families.”
This linear approach works by trial and error: you tweak your wording or add a keyword until you land on the answer you need. It is predictable and manageable to measure, but it can be slow. Users sometimes miss critical angles simply because they do not know the right words to try.
AI Mode and Query Fan-Out
Google’s Query Fan-Out is an AI-powered search technique that changes the way results are generated.
Instead of running a single query and returning a list of links, AI Mode breaks a user prompt into multiple related searches, runs them all simultaneously, and then weaves the findings into a comprehensive answer.
This method aims to give more in-depth and personalized results than traditional search.
Analysis
Google’s AI-first examines the user’s initial query to spot the key aspects and dimensions. It looks for intent, context, and any qualifiers that hint at what the user wants.
Decomposition
Next, the system breaks down the original query into smaller, more focused subqueries. Each subquery targets a specific facet of the topic.
For example, a question about “healthy family meals” might spawn subqueries on prep time, dietary restrictions, and kid-friendly recipes.
Parallel search
All of those subqueries run simultaneously across a variety of sources, including websites, forums, and databases. Running in parallel saves time and ensures the AI gathers insights from every relevant angle.
Result synthesis
Finally, the AI merges the outcomes of each subquery into a single, coherent response. It combines summaries, data points, and citations into one succinct answer. That way, users receive a richer, more comprehensive reply without having to click through multiple pages.
Project Mariner
Project Mariner is Google DeepMind’s experimental AI browser agent that can understand web pages, plan multi-step actions, and carry them out on behalf of the user. It can handle tasks such as online shopping, booking reservations, or filling out forms by navigating websites, retrieving data, and executing commands.
When integrated with AI Mode, Mariner extends Query Fan-Out beyond information gathering to task execution. As AI Mode spins off subqueries to cover every angle, Mariner agents can not only fetch details but also perform actions such as reserving tickets or making purchases.
Its Teach and Repeat feature lets users demonstrate a task once and the agent will replicate it for similar queries in the future. This combination means AI Mode can deliver answers and complete tasks in a seamless, single step.
Implications for SEO and content strategy
With Query Fan-Out, content creators must address a broader range of user needs on a single page rather than relying on individual follow-up queries.
That means writing articles that address every likely angle, using clear section headings or an FAQ format so that AI Mode can easily surface each interpretation when it expands. Analytics teams also need to adapt.
Instead of tracking only the exact search terms users typed in, they should monitor session behavior to catch new variations that emerge from AI-driven conversations.
Continuous testing is crucial, too. By submitting the same prompt repeatedly and logging the AI’s reported subqueries over time, patterns will emerge even if individual runs vary. Finally, focusing on user intent remains key, content should speak directly to the needs behind a query, not just stuff in keywords, so that AI Mode recognizes and rewards beneficial, broad-angle coverage.
Conclusion
Search has moved from a linear drill-down to a branching exploration. Query stacking was predictable and manageable to measure.
Fan-out in AI Mode is richer but less consistent. As Google’s AI takes on more of the search journey, content creators must adapt. Cover all common angles, track new patterns, and keep testing. That is the best way to stay visible in an AI-driven world.