What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content is content appearing over the web in more than one URL. There are two types of duplicates: the internal duplicate content which is on your own website and external duplicate content which is very similar content between several websites. We will talk only about internal duplicates because according to the way that search engines work,unless you copy and paste large piece of content from a third party website, external duplicates won’t harm your SEO.
How are Search Engines identifying duplicates?
There are a lot of scientific methods to help bots identify duplicates but, among all solutions, the Simhash method is the most scalable and efficient way to interpret them (oh yes and published by Googlers). That’s why we implement the simhash method within Oncrawl.
In just a few words, the simhash method aims at computing a fingerprint for each page based on a set of features extracted from a web-page. These features can be keywords (n-Grams), or in some cases HTML tags. Then all fingerprints (all web-pages) are compared to each other to evaluate the « Hamming distance » , i.e evaluating the differences between pages. If two fingerprints are similar, then the content located on these two pages is similar. This way, search engines can group pages by similar content. That’s what we call « clusters of duplicated pages ».
The problem for a search engine such as Google is to decide, within the cluster, which page to index and add in its SERPs. There are several cases :
- Google can decide not to index the pages within a cluster
- Google can decide to index only one of the pages within a cluster
- Or it can decide to index them all but will lower their quality score so that they won’t rank at all
Running this kind of method is very expensive when you need to run it over the world wide web, so Google is often choosing not to index them at all.
Is internal duplicate content a big issue for my website?
Google is smart enough to interpret other factors than semantic analysis to decide which page should be indexed, so you could let it do its job.
But it’s a very bad sign: it’s a point against the site as a reliable source of content, and it will impact its quality score. So having duplicates will lead your website to have lower rankings and crawl frequency applied by Google.
The main thing here is that Google hates wasting its crawl ressources on pages identified with a low value. So that having duplicates will lead Google to fetch less pages on your website, and probably not to crawl your whole website.
How to spot my Near Duplicates?
For obvious reasons, I think Oncrawl is a good way to perform this operation ;-). We are the very first in the world to release a Near Duplicate Detector.
It’s very important for you to take action on your near duplicates. Having an comprehensive view of your clusters of near duplicates will help you validate your strategy. Here are your options:
- Delete your pages with duplicated content and add 301 redirects to unique content
- Put a no-index on duplicated pages
- Set up a canonical on duplicated pages pointing to the original piece of content… But be careful, you should use it with a deep knowledge of what you are doing, because if you are not doing this correctly, it will not have the impact you want.
Indeed, the canonical rules you set-up have a huge influence on GoogleBot’s behavior.
The best practice is to set-up a unique canonical for each cluster of duplicated pages. If not, it’s chaotic.
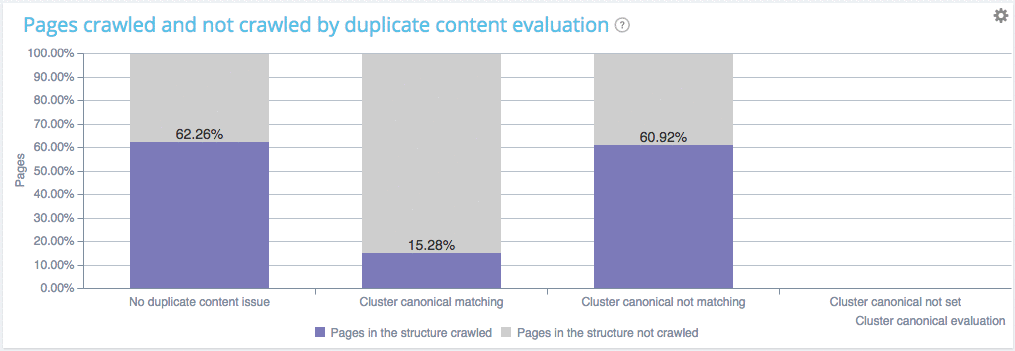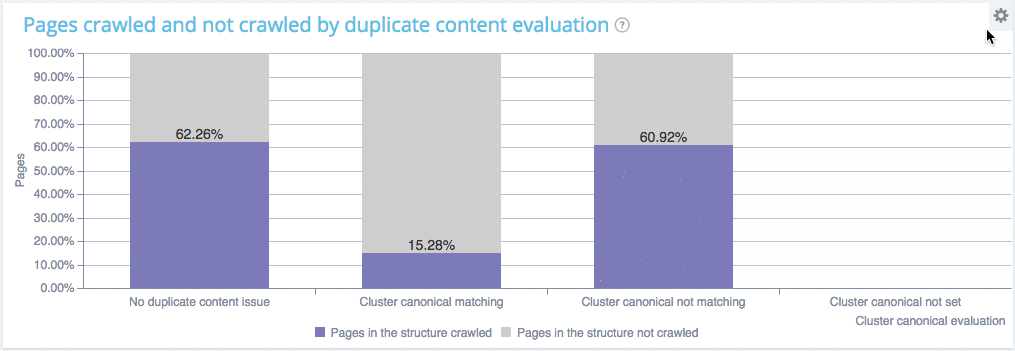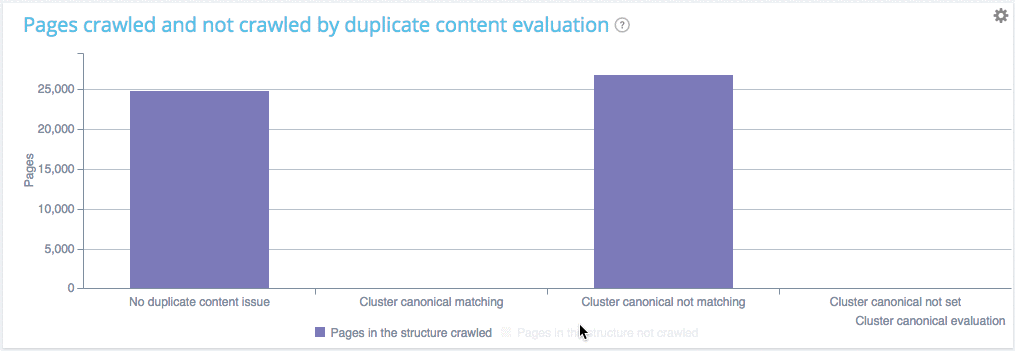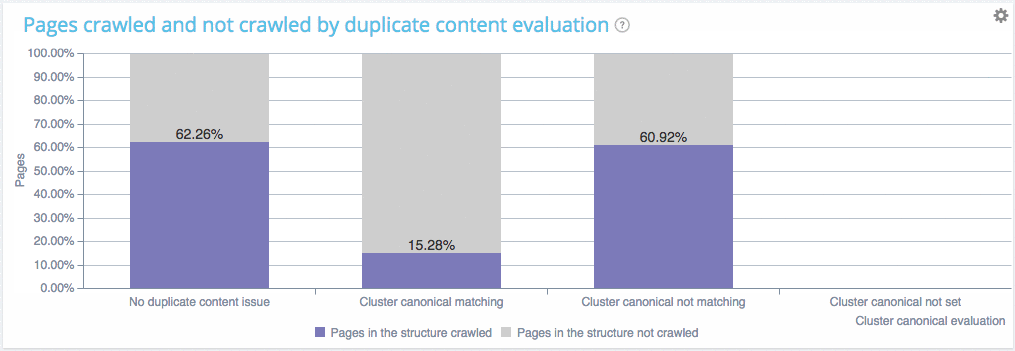
Here is a quick example of what you can find in our combined analysis (comparing crawl vs log data):
You can see on this website that :
- Pages with no duplicate are crawled at a 62.26% ratio
- Pages within clusters of duplicated pages with a canonical are crawled at almosr the same ratio (60.92%). Which means that Google is fetching those pages as usual, to check if you have changed something and thus is wasting its ressources. You crawl frequency will soon decline.
- Pages within clusters of duplicated pages with a unique canonical are not crawled, good job you don’t waste Google ressources.
Conclusion
Fixing your duplicate content issues can take a lot of time depending on what caused the duplicated content to appear. But taking the problem seriously and take action today can generate some of the biggest ROI. Avoiding duplicate content can lead to :
- Better rankings within weeks because of a better website quality score
- More pages ranked in SERPs because of Google allocating its ressources to other parts of your website.