The digital industry can sometimes be ruthless, and some competitors don’t play fairly. Imagine waking up to find your website ranking has nosedived overnight, not because you’ve used bad SEO techniques, but because a competitor decided to sabotage your success.
Negative SEO attacks are a dark reality. 61% of websites have been victims of the invisible enemy working behind the scenes with a sinister motive to cripple their online presence. Such an act jeopardizes years of optimization efforts.
Let’s explore the different kinds of negative SEO attacks and most importantly, what you can do to counter them.
What are negative SEO attacks?
A negative SEO attack uses unethical and manipulative SEO tactics to sabotage a competitor’s website rankings, offsetting their legal SEO efforts. SEO sabotage can comprise the use of spammy links, hacking, smear campaigns, and even duplicate content to push your site out of the SERPs.
The ultimate goal is to signal to search engines that your site is using spamming techniques that are against search engine policies or to convince users that your site is a low-quality one.
In this guide, we will walk you through the different types of negative SEO attacks, how to detect and counter them, and the proactive measures you should put in place to prevent SEO sabotage.
Types of negative SEO attacks
SEO sabotage takes different forms, but they all have the same goal – to ruin your SEO metrics. It’s important to be aware of the various types of negative SEO attacks and how to detect them.
Link farms
A link farm is a group of sites linking to one another with the aim of boosting their respective rankings. They can also be used to maliciously target your site with a number of undesirable backlinks.
Link farms rely on the premise that the more links a page has pointing to it, the more authority it has as viewed by search engines. Link farm creators may do it manually by linking to each other or automate using software to artificially inflate site metrics.
This strategy was only relatively effective in the early SEO days when link farming was an easy way to manipulate search results. Algorithms have advanced, rendering the effectiveness of link farms redundant.
Link farming is now a manipulative black-hat SEO approach and the practice is clearly discouraged in Google’s policy documentation. According to the Google 2022 SpamBrain update, its algorithm ignores and penalizes such links.
[Case Study] A strategic approach to managing volatile pages
Though one spammy link might not throw your site ranking into disarray, if Google does discover a link farm, it will likely penalize it as well as the sites to which it links; that is to say, potentially your site. So what’s your best bet? Try to completely avoid all spammy links.
You don’t have to accept your fate if you’re a victim of malicious linking. There are certain things you can do to counter the potential negative effects.
- Leverage content: Write high-quality and unique content that offers value to your users. This not only promotes natural backlinking but also organically boosts your site rankings.
- Capitalize on social media: Actively engage your brand on social media to anchor your brand image in users’ minds, direct traffic to your site, and foster organic growth.
- Guest blog: Look for a credible and relevant website in your niche and try guest posting. This way, you’ll organically build quality backlinks and brand authority.
- Influencer network: Partner with influencers who align with your brand to spread the word about it. Your brand could potentially gain recognition and build organic backlinks.
Content scraping
Content scraping is the practice of copying original content from a website and posting it elsewhere. It’s simply a low-effort strategy for content scrappers to get free content.
Though their intentions might not be to harm your site, scraping will probably cause you some losses. In a report that delves into the impact of content scraping, we learn that 54% of businesses lose 6% of earnings due to content scraping.
When Google comes up against duplicate content, it only picks one content version to show and might even display the scraped version. If you’re the original creator and this happens, your site may lose considerable organic traffic.
Smear campaign
A smear campaign is a tactic competitors use to spread damaging information about your business. It lowers the chances of your site being ranked in the SERPs and it reduces click-through rates.
Competitors can use this tactic by:
- Creating fake, negative reviews on social media, on online communities like Reddit, or on aggregate review sites;
- Using influencers to spread fake information about your business;
- Impersonating you across different digital platforms.
You can manually search online or use a brand mentions tool to check where your brand has been mentioned.
Keep in mind that not every negative mention is a negative SEO attack. Some are genuine reviews from unsatisfied customers. In that case, you should address the issue and offer a genuine and friendly resolution. If it’s a negative SEO attack, then report it to the platform’s administrator.
Hotlinking
Hotlinking or leeching involves using another site’s bandwidth to display resources such as video, audio, or an image through a direct link to the original site. The linking site shifts the hosting service cost to the original site whenever a browser tries to fetch these resources.
Simply put, in hotlinking, a website evades the burden of hosting these resources and steals another site’s bandwidth while freely benefiting from that site’s content.
Hotlinking can impact your site’s performance by lowering load time as it tries to fetch resources in real-time. This, in turn, negatively affects user experience and your site’s rankings.
It can also increase your costs associated with your host server and you may be more vulnerable to malicious tactics like content and imagery misrepresentation.
Hacking
Whether you work in SEO or not, you have likely heard of hacking. This is an effective attack by which a hacker gains access to your site with the intent of pirating information or causing damage. This can include:
- Injecting spyware or malware
- Deleting or adding duplicate content
- Modifying your
Robots.txtfile to prevent crawling - Diverting your URLs to spammy links.
Hacking is an extremely dangerous type of attack, and it can be hard to detect early. For example, hackers can make small but dangerous website modifications that add up over time, and before you realize it, the damage is already done.
According to a 2024 IBM report, the global financial impact of data breaches averages $4.88 million, the highest ever reported.
Notably, the financial impact is limited not only to the immediate loss, but also the long-term cost you incur recovering lost traffic, rebuilding your brand reputation, and deploying technical solutions to remedy the vulnerabilities.
How to detect negative SEO attacks
Though attackers don’t warn you before attacking your site, having negative SEO knowledge allows you to spot attack signs and counter them. Let’s look at the various mechanisms you can use to detect SEO sabotage.
Identifying link farms
To spot link farms, look out for these signs.
- Basic template design: Link farms typically use simple designs compared to high-quality websites. The owners rarely want to spend money on their website, so they tend to use the template provided by their hosting company with little to no modifications.
- Many unrelated topics: Link farms’ main goal is to cash in on their links, meaning they can direct backlinks to any website as long as they get paid. You’ll notice these sites have various articles on diverse topics, especially on competitive niches, which is a red flag.
- Inferior articles: Their guest posts are intended to conceal links to other sites and are not meant for users’ consumption. You’ll discover these articles are very generic and of poor quality since the content creators want to cut costs.
- Unknown authors: The articles’ authorship is concealed as either a “guest writer” or “Team (site Name).” No competent writer would ever want their names looped in poor-quality content.
- Several outbound links: Typically, link farms link many unrelated websites using keyword-rich anchor text.
Detecting other negative SEO attacks
Beyond link farms, here are signs to look out for to detect other negative SEO attacks.
Watch out for spam link attacks
Check if there are fresh backlinks directed to your site. Ahrefs allows you to establish backlink alerts and sends discovered backlinks to your email. You can also use its “site explore” feature to detect any increase in your backlink profile or manipulation of your anchor text ratio.
Keep an eye on your site’s traffic and bounce rates
By constantly monitoring your site’s traffic and user engagement with tools like Oncrawl’s SEO log analyzer, you are able to see when the changes actually occur and consequently evaluate what coincides with them.
Whether it’s issues regarding your crawlability, indexing, or external intervention, the tool gives you a wealth of data that can facilitate your analysis.
Investigate spammy comments
A spike in spammy comments directed to your brand but not tied to customer dissatisfaction may be a potential sign of a SEO negative attack. These damage your brand reputation and potentially decrease engagement metrics.
[Case Study] How OMIO uses Oncrawl to improve website quality
Check for duplicate content
One simple way to check if your content appears elsewhere is to copy and paste a chunk of it to a search engine and see what the search results show you.
A wide range of AI tools like Copyscape, Grammarly, and Turnitin have made the work simpler, allowing you to scan your content against billions of web pages to detect and address duplication.
If you have duplicate content within your pages, tools like Siteliner or Quetext go a step further to analyze internal duplication, ensuring your pages don’t cannibalize one another.
Track your loading speed and overall website performance
A sudden reduction in loading speed could be the result of a number of problems. Have you considered that it may be a sign of a distributed denial of service (DDoS) and a part of a strategic attack on your site? You can also use Oncrawl to monitor your site’s performance and get notified when a performance issue arises.
Be on the look out for social impersonation
Keep an eye out for attackers who may impersonate your brand using fake social accounts. Conduct regular online scans for fake accounts and report them to prevent damage to your brand’s trust and reputation.
How to counter negative SEO attacks
Disavow spammy links
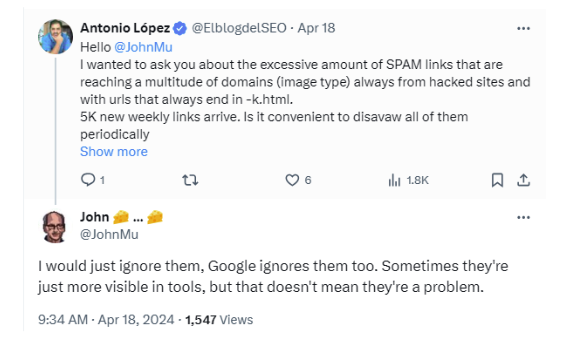
As per Google guidelines, you should disavow spammy, low-quality, and artificial links if they are considerable in number or are likely to earn your site a manual action.
To disavow, you need to submit a list of pages or domains telling Google you don’t authenticate them, and it should ignore them.
On the other hand, Google’s Penguin 4.0 core algorithm is the main one used for devaluing spam, so you could choose to not disavow spammy links unless you are in a competitive vertical or the links cause a significant drop in your traffic.
Here’s Google’s John Mueller’s position concerning the issue.
Since Google ignores spam, you could choose to do so too.
Secure your site
In 2023 alone, 6.06 billion malware attacks were tracked globally, with websites being the leading gateway for phishing attacks. Take a look at the trajectory of malware attacks over the years.

Source: Statista
Therefore, to safeguard your site from SEO sabotage, here’s what to do:
- Conduct periodic website audits to spot any performance abnormalities and promptly address them before they significantly lower your SEO metrics.
- Enable a two-factor authentication to trigger an input code for every login attempt.
- Activate Google Search Console alerts to get updates on any security breaches.
- Use strong passwords to fortify security measures and make hacking more difficult.
Use hotlinking countermeasures
Here are actionable tips to safeguard your digital assets from hotlinking.
- Use
.htaccessto control domain access to your website resources and block hotlinking from URLs you’ve not allowed in your “Domain.com” field. - Check your hosting control panel for in-built hotlinking protection service and click enable to activate the service.
- Utilize content delivery networks (CDN) with a hotlink protection service to provide a barrier between your site and the hotlinker.
- Explore your content management system (CMS) for features and plugins offering hotlink protection.
- Use
ApacheorNginxto modify your server configurations and deter other domains from accessing your resources. - Always monitor your server logs for abnormal bandwidth utilization to allow you to detect potential hotlinking.
Clean duplicate content
If your content has been republished on another site, contact the Webmaster for content removal. If this doesn’t work, submit a DMCA takedown notice or report to Google.
Also consider appending copyright notices to your website to caution other site owners against duplicating your content.
Proactive measures to prevent negative SEO
You’ve likely heard the expression, “prevention is better than cure”. Well, it holds true here. Proactively preventing SEO sabotage can save you significant time and resources in remedying its damage. Here are practical tips to remain vigilant.
- Use secure hosting: Ensure your choice of hosting service is comprehensive and protects your site against illegal access, DDoS attacks, and malware injection. The hosting package should also include periodic backups, allowing you to restore data to a secure state in case of an attack.
- Utilize HTTPS and secure protocol: Since HTTPS utilizes SSL/TLS encryption, running your site on it ensures encrypted data between your site and users. Besides, Google considers HTTPS a ranking factor, a stance dating back to 2014.

Source: Google Search Central
Though Google didn’t explicitly mention HTTP among its current ranking signals, that doesn’t mean you should ignore it, at least as a security measure.
Besides, Google lists security as a vital metric in its guidelines regarding self-assessed page experience, highlighting the need to secure your site and enhance user experience.
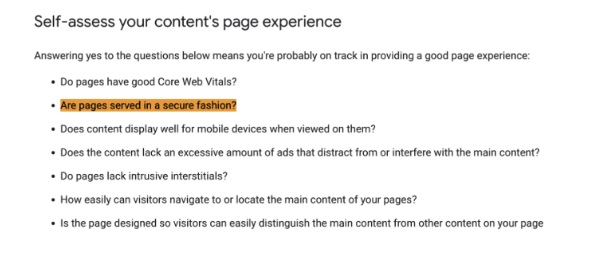
Source: Google Search Central
Key takeaways
At the end of the day, being vigilant about negative SEO attacks is not just a “nice to have” – it’s highly recommended. The earlier you detect these attacks, the better you can protect your website and save yourself the optimization losses – which could represent years of SEO hard work.
Climbing the ranks is a healthy SEO strategy, but keeping the metrics and protecting them from rivals who may try to knock them out is what matters most. So, be on the look out! Periodically monitor your site, fortify your security, and seal all weak points. Remaining proactive may be your best bet to counter SEO sabotage – and your business will be better off for it.