Considering how much Google’s approach to evaluating content quality has changed since the original Panda algorithm was introduced in 2011, we thought it was important to take another look at how you can identify and fix any poor content on your site.
Content quality is assessed through a sophisticated combination of algorithms rather than a single update. Since 2011, there have been a number of updates, but one that stands out is the Helpful Content Update that was first released in 2022.
After its launch, a number of sites were hit hard as the algorithm apparently deemed that their site’s content was not high-quality and user focused.
Since then, there have been a number of iterations of the HCU and SEOs have become more sensitive to what makes the cut and what doesn’t.
When auditing your website, it’s necessary to evaluate content quality and check if you have thin or poor quality content appearing on your pages as it can impact your search rankings and your visibility in AI responses.
In this article, we will look at the current content quality standards and walk through actionable steps you can take to identify and fix problematic content on your website.
What you should know about how Google evaluates content quality
Google’s original Panda algorithm, which targeted thin and low-quality content, has been a fully integrated part of Google’s core ranking algorithm since 2016. Today, content quality assessment has expanded far beyond the original Panda parameters and includes:
- Helpful Content Update: This system specifically targets content created primarily for search engines rather than humans.
- E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness are key factors in determining content value.
- AI content evaluation: Google’s quality raters are now assessing AI-generated content.
- Page experience signals: Including Core Web Vitals and mobile usability.
Why content quality matters
For Google, thin content, or poor content, means either you have pages with a low proportion of copy compared to image/navigation elements, that your thin content could be duplicate or similar content (both internal or external), or that it offers little to no value to users.
Poor content quality can severely impact your site’s performance in several ways including:
- Lower rankings across your entire site (not just the problematic pages)
- Reduced visibility in featured snippets and other SERP features
- Diminished site authority
- Higher bounce rates and lower engagement
- Difficulty ranking new content, even if it’s high-quality
If you think you or one of your clients are in this situation, you will need to spot it, correct it and quickly show Google (and now AI search), that you have made the right changes.
The first step, spot your thin or poor content with Oncrawl.
Identifying low-quality content on your website
Launch a full-site crawl
Launching a crawl of your full website with Oncrawl will allow you to analyze the entirety of your site’s content.
Make sure you have connected your Google Analytics and Google Search Console (GSC) accounts to your Oncrawl account for a thorough analysis.GSC provides data related to indexing and performance while GA4 will give you a clearer picture regarding user engagement metrics.
Find thin content with Oncrawl’s crawl report
In the Content section of your crawl report, you can identify how many and which pages have thin content or duplicate content. You can also analyze what the word count distribution looks like for your site.
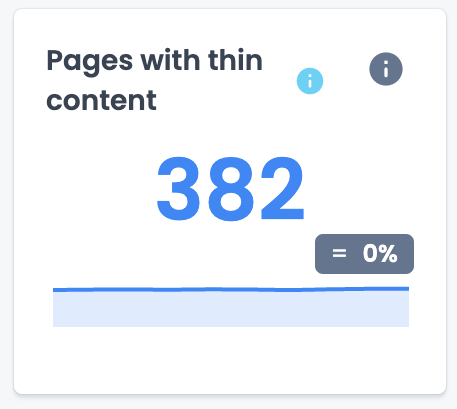
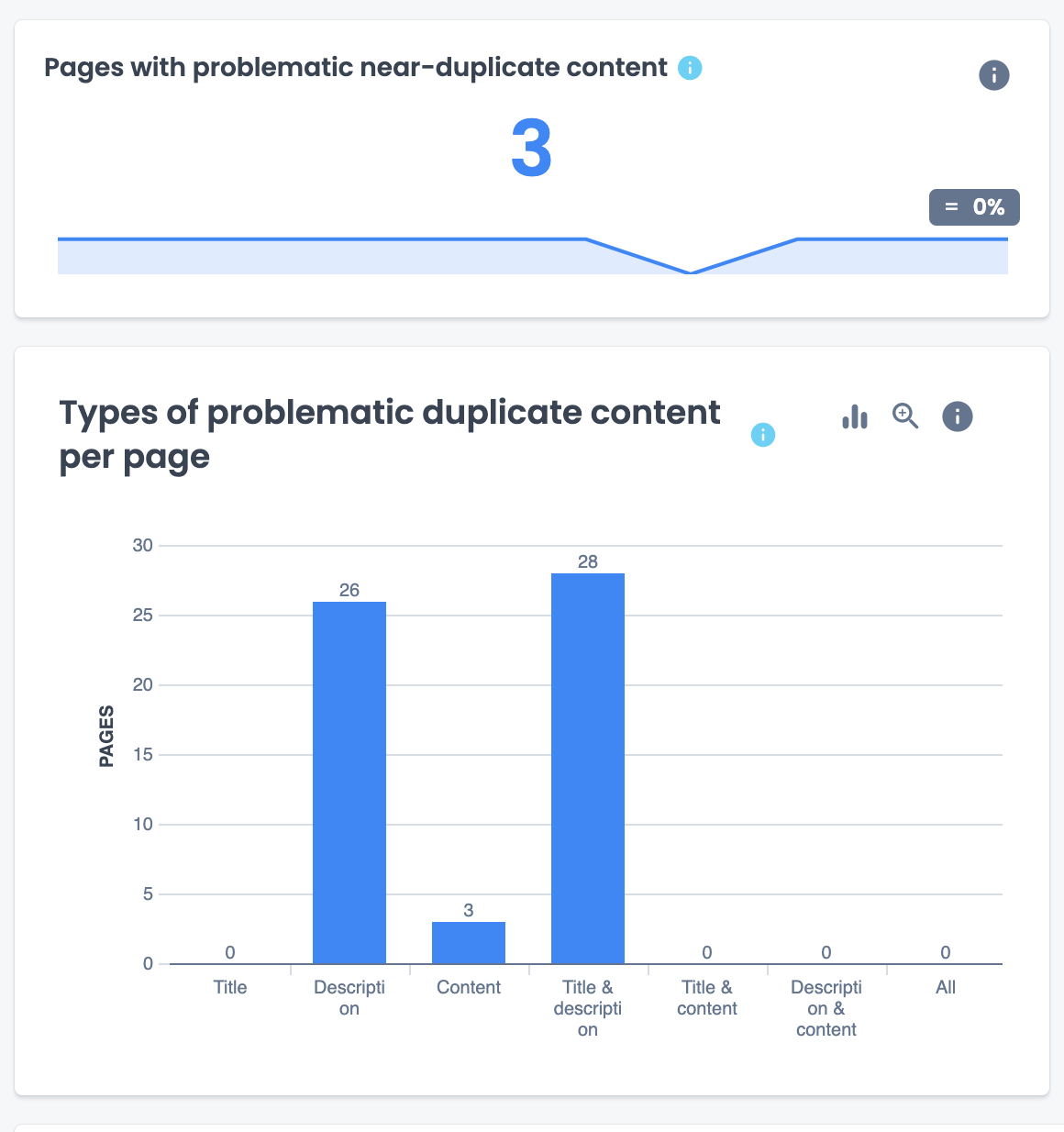
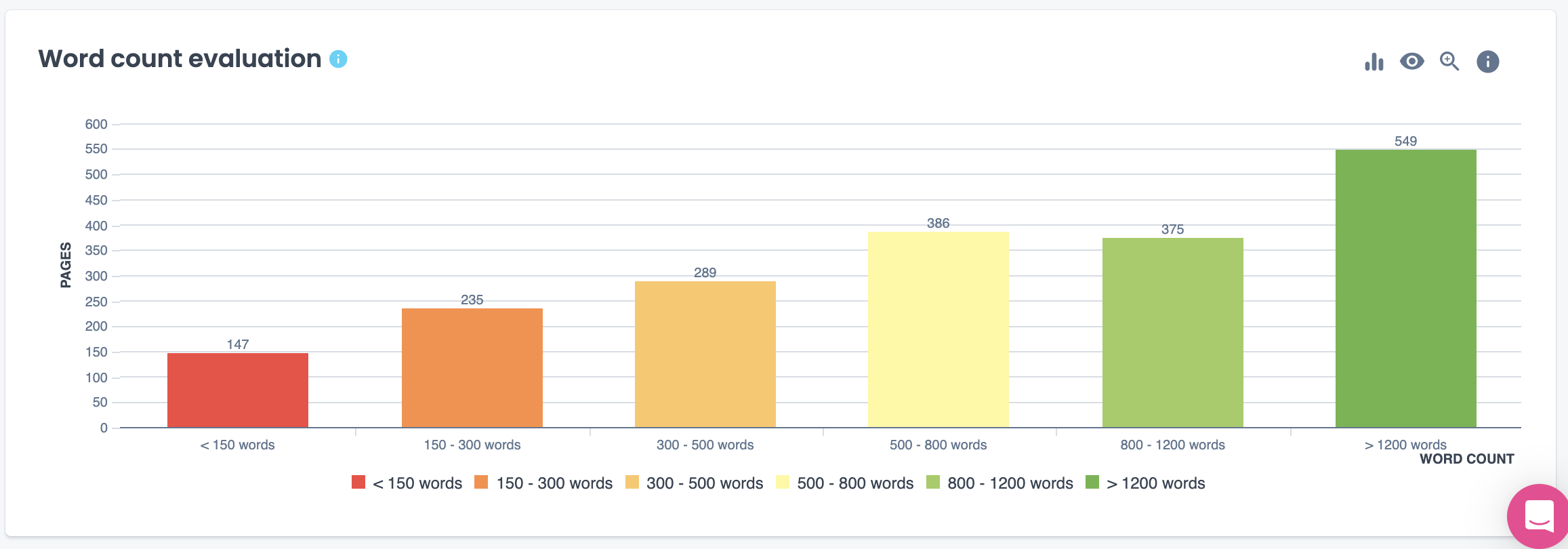
In the SEO Impact report, that cross analyzes your site’s data with GA4 analytics, you can also identify if there is any correlation between thin content and your site visits.
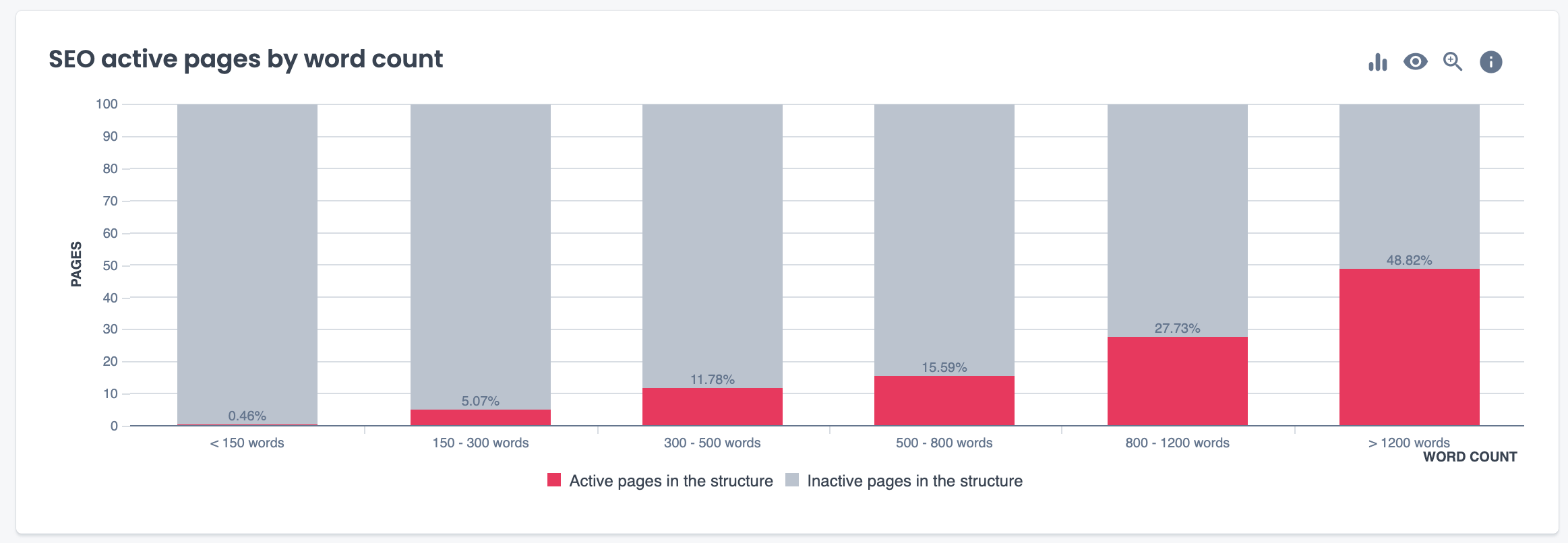
Evaluate poor-quality content with multiple metrics
Analyzing your pages based on metrics such as bounce rate and the time users spend on pages can also help you zero in on low-quality sections of your site.
In your analysis, consider looking at:
- Organic traffic: Pages with declining or zero organic traffic
- User engagement: High bounce rates, low time-on-page
- Keyword relevance: Content targeting outdated or irrelevant keywords
- Duplicate/similar content: Internal and external content similarity
- Technical issues: Slow loading times, poor mobile experience, accessibility issues
- Outdated information: Factually incorrect or outdated content
Action plan to manage poor content
Once you have identified your poor quality or thin content, the next step is to prioritize what you will fix first.
Based on the resources you have available, step one should be to start with the pages that are bringing in organic traffic and pages that have strategic importance.
Improve valuable but underperforming content
For content that’s strategically important but performing poorly, there are a number of steps you can take. Start by updating the content with current information to ensure accuracy. Consider expanding the scope of the content to be more comprehensive, filling in the gaps that may exist in the original content.
Additionally, you can improve the overall structure by incorporating clear headings and better formatting that enhances readability and user experience.
Next, strengthen the content’s SEO performance by improving internal linking both to and from these pages.
Finally, update publication dates when significant changes are made to signal, to both search engines and users, that your content is fresh.
[Ebook] Technical SEO for non-technical thinkers
Consolidate similar or overlapping content
If you have identified multiple pages on your site that have content covering similar topics, you will need to identify the strongest performing page as the primary URL and then merge unique and valuable information from weaker pages.
Set up 301 redirects from consolidated pages and update internal links to point to the primary URL.
Remove or no-index pages with thin content
After you’ve implemented all the steps above, you may find that you still have pages with limited value that cannot be improved.
In this case, you can apply noindex tags to remove them from Google’s index. Use canonical tags when appropriate to point to stronger content. You can also remove the page altogether if the content serves no user purpose.
Ultimately, this will avoid search engines and users landing on those pages.
Monitor your changes
Continue to run multiple site crawls to track your site’s performance and see if your changes are having the intended impact.
However, keep in mind that SEO changes don’t take place over a matter of days, it could be weeks to see changes. Keep track of what works and make additional adjustments where necessary.
Closing thoughts
While search algorithms continue to evolve, they seem to be moving in the same direction: toward providing quality content that actually benefits the users.
Content quality assessment has evolved far beyond the original Panda algorithm, but by implementing a regular content quality audit and taking steps to deal with problematic content, you can improve your site’s overall performance and build long-term search visibility.
Remember that Google’s systems look at your site holistically—maintaining consistently high-quality content across your entire domain is the key to sustained search success.

