Article updated on May, 2018
Following your feedbacks and questions about this article, we wanted to specify some terms and reformulate some sentences which were a bit misleading.
Whether you display product listings on your e-commerce website, series of posts on your forum, or you have segmented your content to make it easier to read, chances are you’ve been using pagination. Pagination and SEO are challenging topic. We are going to see why and how to handle SEO issues due to pagination several parts articles.
What are the main SEO problems you got with pagination?
Crawl limitation
You’ve been aware that Google has a kind of “crawl budget” to index your website, and your goal is to optimise this budget. You don’t want Googlbots to get tied up in your paginated pages if your page 2, 3, 4… don’t add any valuable content. This is often the case when browsing a paginated thread in a Forum.
InRank dilution
Call it InRank, Internal Pagerank, or Page Juice, we mean the way authority spreads within your website. If you didn’t think your pagination with InRank in mind, you might be loosing some juice. Indeed, an incorrect code implementation can dilute how popularity flows within your paginated pages.
Duplication & Thin content
In some cases — mainly product listings and forum threads — paginated pages have often a similar title than page 1, and the content displayed is often less unique than the pieces you got in page 1. So this makes your paginated pages great candidates to get flagged as near duplicates by search engines. Pagination often displays thin content which can impact how qualitative your website is in the eyes of Google. So be careful about low quality content due to pagination.
Fortunately, Google has some guidelines about paginated content which is telling us:
Specify a View All Pages of the Article
It’s good for the bots to get all parts of an article instead of having to paginate the article to get the complete view, so Google recommends to have a version of your paginated content on one single page. But sometimes it’s bad for user experience. I love the way Business Insider has done the job. For their slideshows, they only let Google index the “One Page” version, and add a rel=“canonical” to the “one page” version for all paginated pages.
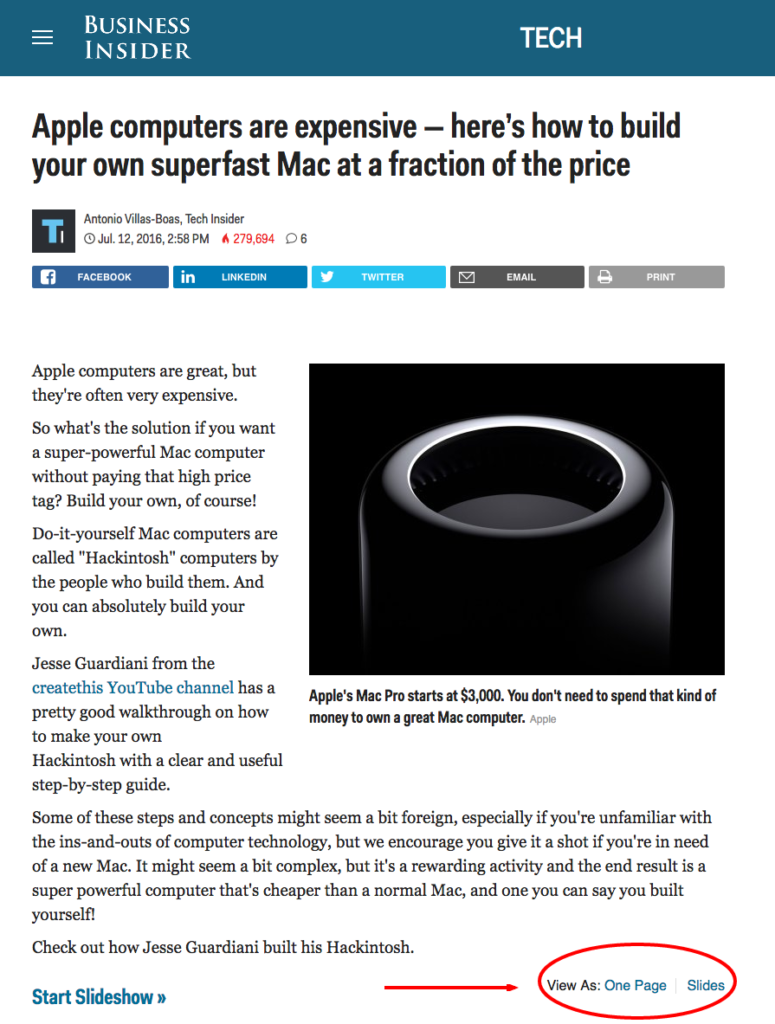
This is very smart and very user friendly.
Use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” links to indicate the relationship between your pages.
Google says:
This markup provides a strong hint to Google that you would like us to treat these pages as a logical sequence, thus consolidating their linking properties and usually sending searchers to the first page.
Be very careful in terms of code implementation, because if Google finds an error in your code, it might not be interpreting your rel=”next” and rel=”prev” links.
This is theory, and you need to get your hands on your website architecture, types of content and strategy to get the perfect pagination specs. So here are a few tricks I used over the years.
My Top 10 Pagination of a several parts articles rules to get your SEO right
1# By default, don’t let Google index the paginated pages (we are only speaking about pages which cut the article in several parts).
2# Only let Google index your paginated pages (from several parts articles) if the content is bold. You can use the number of words on your paginated pages to sort them.
3# Always add a Canonical to page 1 on all your paginated pages.
4# Put nofollow attributes on all links which point towards paginated pages in the case of an article in several parts.
5# Configure the URL parameters in your Search Console.
6# Setup your URLs for paginated pages of a several parts articles so that you can easily add a rule in your Robots.txt not lose crawl budget on these pages (which are already canonicals towards the page with the full content).
7# Add a no-index, nofollow in your meta-robots, just to be sure.
8# If you are not following the previous rules, be conscious about the quality of your content. Specify some rules to let Google index your paginated content if you are sure it’s adding value to your users, and that it’s unique.
9# Never add the urls of the parts of your paginated articles in your Sitemap.xml.
10# Don’t show links to page 2, 3, 4, 5… 10, 11, 12… at the end of your content but only a link to the next and previous pages so that you won’t dilute your page authority.
Bonus
Sometimes you need to manipulate your internal linking structure to boost the popularity (Inrank) of groups of pages on your website. You can change the nofollow attribute to follow on paginated pages to get more pages candidates to add links to your main content.
Pagination is not easy and you should write down a plan that matches your business strategy.


Hello!
Robots.txt prevents from crawling, not from indexing, so you won’t deindex those pages by adding rules in your robots.txt file.
Nofollow rules won’t let bots crawl resources from your pagination. As you know, pagination helps search engines discovering website content, then with this rules, you’ll just stop them doing it.
(non exhaustive comment)
Hi Anthony, you can add noindex directives to your robots.txt too. Not many people are aware of it, but you can use it for deindexing too.
Noindex + canonical is dangerous! “Page 1” can be unindexed.
To include or not links to some pages must been also considered from a traffic point of view. Linkjuice is not the unique factor.
Hey Jan-Willem,
I’m sorry, but it’s false. I’ma show it with the following example:
https://www.seroundtable.com/boyfriend-spammed-12909.html
is “disallowed” for all bots in the robots txt file: https://www.seroundtable.com/robots.txt,
User-agent: *
Disallow: /boyfriend-spammed-12909.html
but if you have a look in the Google index, for instance:
https://www.google.fr/search?q=inurl%3A%2Fboyfriend-spammed-12909.html&oq=inurl%3A%2Fboyfriend-spammed-12909.html&aqs=chrome..69i57j69i58.1631j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
You then can see this resource is still indexed.
;)