A comprehensive guide of the best way to use Google Search Console for effective SEO and successful conversions from 100+ marketers.
We studied the opinions of 100+ marketers who shared online about how they use Google Search Console to improve their SEO. This article contains synthesized expert advice and a few detailed instructions.
There are many SEO tools available for you to use.
G2 says that there are about 200+ of them and most of which come at a cost. Each tool has its own data set and unique metrics. You might be asking yourself which one you should employ in your marketing.
One of the best tools that can handle your keyword and SEO ranking is Google Search Console. It can help you with tons of work, and it comes for free.
You might know how to use this tool, but experts have mastered it.
We sought 100+ marketers how they go by and collected tips to create this guide. This will help you get the best out of Google Search Console for SEO.
You must learn first about the essential data and how to find it. Then, you’ll have insights from the 100+ experts who advise the best ways you can use Google Search Console to gain traffic and top rankings.
Contents:
- 35 Expert Tips On Using Google Search Console for SEO
- 10 Advantages of Using Google Search Console
35 Expert Tips On Using Google Search Console for SEO
- Know what your vital SEO metrics are.
- Avoid falling into the data trap.
- Take your data outside of the tool.
- Track the performance of local keywords.
- Study the countries tab.
- Look into the mobile vs. desktop traffic.
- Look at the parts of your website in detail.
- Mitigate keyword cannibalization.
- Compare keyword predictions with real-time rankings.
- Check for website coverage problems.
- Submit new URLs for the tool to inspect.
- Inspect the canonical domain settings.
- Replace meta tags and monitor CTR impact.
- Watch high CTR keywords closely.
- Find great topics.
- See how your data compares to competitors.
- Check your click-to-lead conversion rate.
- Monitor your most popular backlinks.
- See site links.
- Seek out internal linking opportunities.
- Monitor the SEO performance of a new website.
- Measure your search performance.
- Collaborate with your team.
- Do not forget that Search Console data isn’t perfect.
- Seek out internal linking opportunities to increase rankings.
- Find out what pages are wasting your budget.
- Identify the ideal target keywords.
- Seek out opportunities to better your CTR.
- Look for pages that require additional optimization.
- Search for keywords to target in paid campaigns.
- Get new content ideas.
- Measure the changes in both branded & non-branded search volumes.
- Decrease the bounce rate by seeking out negative keywords.
- Give Google additional information without adding structured data.
- Use other tools alongside GSC.
Know what your vital SEO metrics are.
Remember that you must not focus on just one metric, as it could be misleading.
The most studied metric is clicks:
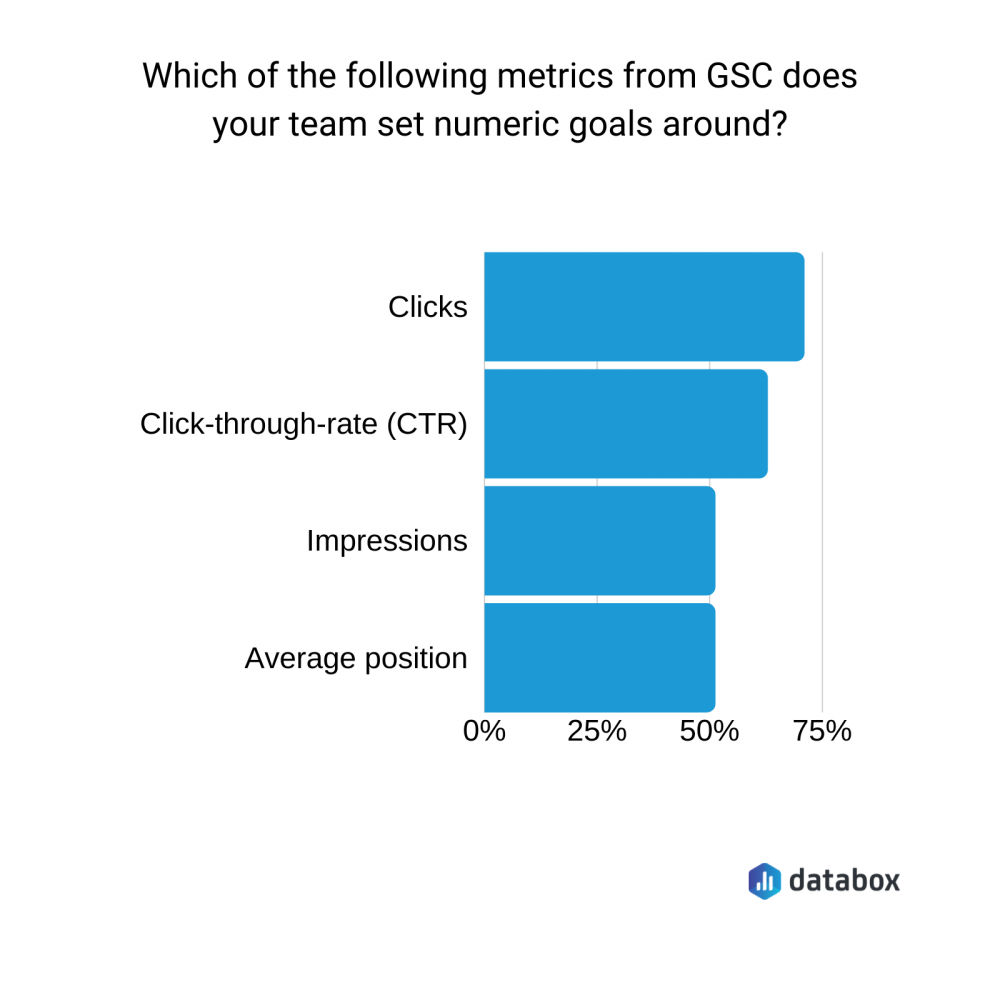
However, experts say that you should look at a combination of impressions, CTR, and average positions. In this situation, clicks are irrelevant as they are merely a result of the KPI of CTR and impressions.
A high number of impressions and an outstanding average position could happen if you rate well for particular keywords, but don’t match search intent. This information can lead you to the wrong impression that it is performing excellently.
Avoid falling into the data trap.
Professional marketers believe in keeping things simple.
GSC has many metrics, and it’s not hard to fall into the data trap.
You must track a few leading terms and metrics. Know your top five search terms, which are the ones that are significantly relevant to your brand and are most likely to drive leads.
Check your data regularly and know how you’re tracking in general. Additionally, you must monitor your vital click and impression metrics and watch the long-term trend line.
Daily fluctuations are normal, but the monthly changes are more crucial. Pay attention to the big picture as much as you do for details. There can be too much data in Google Search Console, and it is easy for anyone to get lost in nuanced decision making.
Consider how you approach your content strategy and how your data informs it. If you are overwhelmed with the amount of data available to you, cut the noise and direct it to the most critical metrics.
Take your data outside of the tool.
Export GSC data for analysis in other tools like Excel or Google Data Studio.
It is simple to export the data from the tool into a document that can cut the data by specific pages, countries, queries, and devices.
Doing this ensures it will be saved. This method allows you to analyze with more sophistication.
Use Google Data Studio to blend data so that you can cross-reference positions with on-site metrics from Analytics and have a much more in-depth insight into performance.
With this strategy, you can see performance trends quickly. For example, you’ll see a % change in CTR or position over a specific period.
Track the performance of local keywords.
You can add a URL query to the primary website field within Google My Business. Afterwhich, use GSC to see what keywords people use to find and click local results.
Use the “Exact URL” page filter in GSC to differentiate a page’s standard organic clicks against its local organic clicks. This method provides information on granular search terms that can be used to increase local SEO efforts.
The SERPs are hyper-localized, and there are massive variations in rankings and traffic down to city and town-level data.
Keywords that you think rank well for the country-wide could be ranking poorly at a local level if local competitors are targeting the same words. You must pay attention to the geographic filters in the tool.
It is best if you integrate GSC into Google Analytics. This method can help refine data affected by location in a much more granular manner.
Study the countries tab.
One expert tip for using GSC to track SERPs is to keep an eye on the “Countries” tab.
Monitor the countries in your SERPs, so that you can adjust your future SEO strategies to target the countries you want.
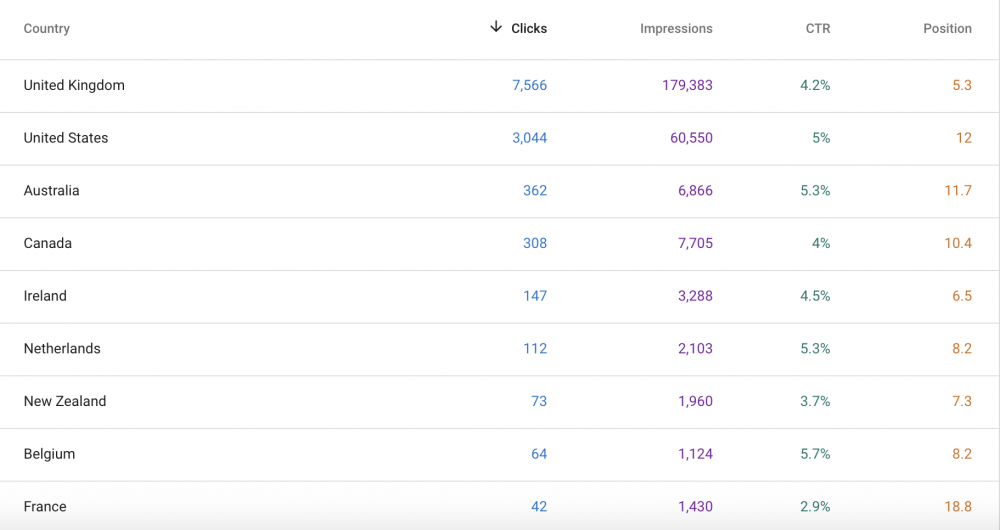
Look into the mobile vs. desktop traffic.
Look at devices in the GSC performance report. Many forget that the majority of their traffic probably comes from mobile devices and that mobile rankings might differ from their desktop rankings.
Look at the devices section to see what devices are driving the most traffic.
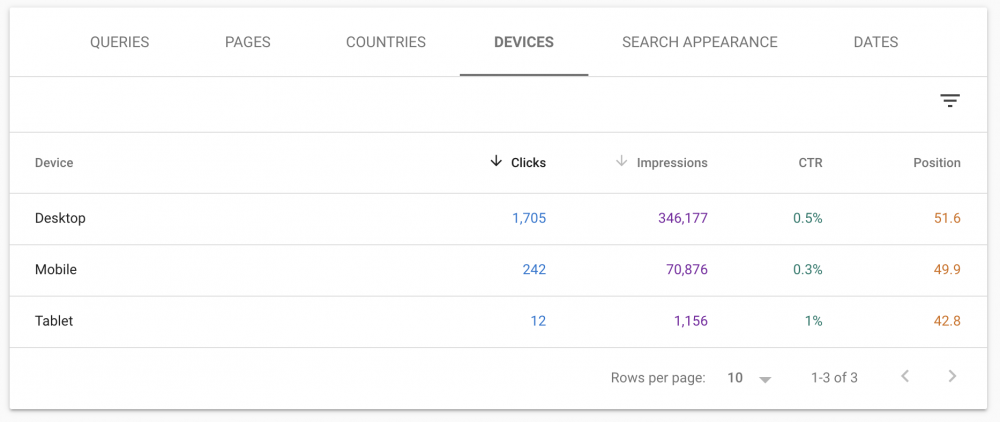
You can pull out excellent reports that will help show you if your SEO is effective. You will see a gradual increase in mobile traffic if you have excellent SEO.
Look at the parts of your website in detail.
An excellent way to start tracking your ranking is by opening the performance report, viewing by Pages (URL), and then clicking the filter button and using include/exclude to monitor individual sections of the website, including /blog/ or /services/.
Then, you can drill down and watch CTR, Clicks, and more across various devices and regions.
Having information across sets of pages can be vital when it comes to reporting.
An excellent tip for using the tool is to focus on user queries in your blogs carefully. Those queries help you master the keyword intent that enables you to refine your blog and rank a lot better.
When your page reaches the top 10, try to focus more on the CTR by manipulating the title and meta.
Mitigate keyword cannibalization.
Marketers recommend that you identify possible keyword cannibalization problems using the “Query” filter. You should view the pages which rank for this term and filter to compare the top 2 pages by impressions using “Compare.”
With the “Impressions” or “Average Position” tab, you will find out where pages dropped in and out of search results for the target term.
This method will not be conclusive in identifying cannibalization issues, but it will set you on your way to spot instances where a page that is starting to rank causes another to drop.
Explore further to determine whether it is a cannibalization issue or not.
Compare keyword predictions with real-time rankings.
Regularly, a few months apart, reassess keyword ranking targets by comparing those you track daily in Ahrefs against those that show up in the GSC report.
With this, you’ll see which keywords you have unintentionally gained traction for. You can focus on efforts to optimize for those themes and spend less energy on issues that you are struggling with.
You must always monitor your keywords. If they do not rank, then you need to pivot and choose new keywords and ensure that your original keywords are proper for SEO.
Check for website coverage problems.
One feature that adds significant value is the Coverage tab. With it, you will identify and track errors that could impact site-wide, search rank, or specific pages. It defines things, including server errors, unindexed pages, crawl issues, unfound URLs, and more. The tool allows you to remediate issues, re-index, and notify Google that the problems are fixed.
In the Performance tab, monitor the number of clicks and impressions of every page you’ve fixed gains after optimizations.
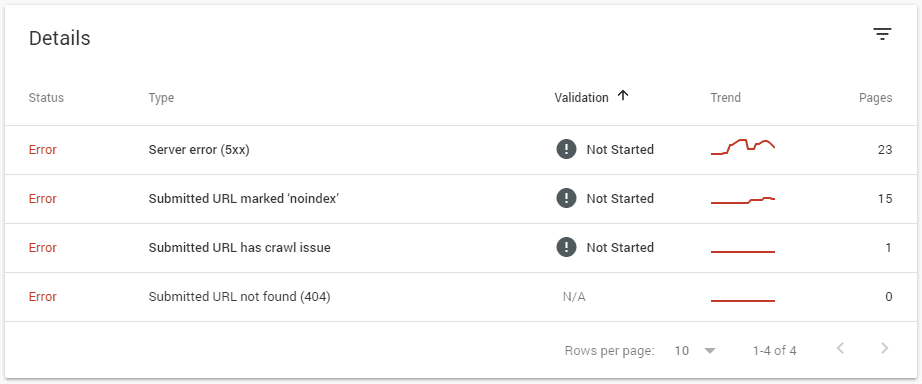
The index status can check which URLs are indexed, blocked, or removed by Google. You can also find out why, correct errors, and make improvements that generate better results.
Use the console to find out website errors, security issues, and indexing problems that affect your rank.
Submit new URLs for the tool to inspect.
Google can take a few days to find your URL. Within that time, you are refreshing your data to check immediate impact. However, there isn’t any as Google doesn’t know that your content exists yet.
After publishing a new post or improving an old one, you must resubmit its URL via the URL inspection tool.
If you do not do this, Google might not notice the changes at once. Get your URL re-indexed as fast as possible.
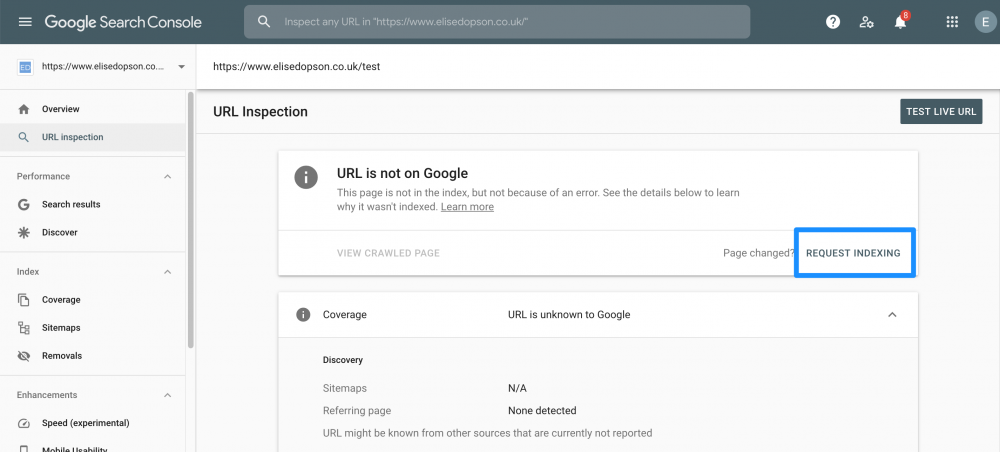
By doing this, you encourage the crawler to review and index your content quicker, so that you can get organic traffic as soon as possible.
Here are two steps you can take.
- Paste the URL of the post/page into the search box, and wait for the page to process your link. Be sure that it has no additional parameters.
- Click “request indexing.” If there are issues, fix the errors first before submitting the link.
You can use Yoast SEO to generate a sitemap that you will submit to GSC. Sitemaps make for easier crawling and indexing.
Inspect the canonical domain settings.
Make sure to select the canonical domain that you prefer.
Specify whether you prefer “www” in front of your domain name or not.
If you don’t do this, Google might see the www and non-www versions as distinct, which means that you will have divided credit for page views, clicks, backlinks, and engagement between two domains. This is disadvantageous to SEO.
Replace meta tags and monitor CTR impact.
Always highly focus on the CTR of your top keywords and pages. With your internal data, you will see that when there is a consistent drive-up of CTR, rankings will improve gradually.
Update the title tag and meta descriptions monthly and run tests to find out if your new copy can better your CTR. It is vital that you also run organic search snippet tests.
This tactic can help you grow your overall traffic.
When you are in the Search Console, click Performance, and filter the Queries list by Impressions. If you find a query that has many impressions, but few or no clicks, it is most likely a keyword you are close to having a breakthrough with that needs just a little more optimization.
You could beef-up the article a bit or try to optimize the title and meta tags. These are straightforward methods for you to get an idea of some posts to optimize. Hence, you could lead to more traffic to your site.
Watch high CTR keywords closely.
In tracking your website in SERPs, you should monitor which keywords have higher click-through rates and optimize around those.
If you are optimizing around two different keywords, you might find that one of them has a higher CTR that can result in more clicks. That keyword can be more favorable even if it has a lower search volume than others.
It is recommended that you optimize and expand old blogs by using keywords that are already working.
Filter your queries by page and find out what terms a blog already ranks for. Look for relevant keywords that rank in positions 8-20, not the words that you weren’t targeting directly, but the content still shows up for.
Edit your blog post and use those terms to expand your content for a boost in rankings.
Experts publish new content at least once a week. That’s a significant amount of material to monitor with the tool.
When you know what keywords you rank for, you can optimize your site to rank higher by matching your content with the targeted keyword. Additionally, you can also track words that have low CTR that you want to rank higher for. When you know what keywords have a low CTR, you can improve them.
It is excellent if you have pages on the first and second positions.
Find optimization opportunities for those in the 3rd position or below, by clicking on the query and going to the Pages Tab. It will show you what page that is ranking.
Check if you can optimize that page by building new links, expanding the content, or improving the CTR by tweaking the meta title and description.
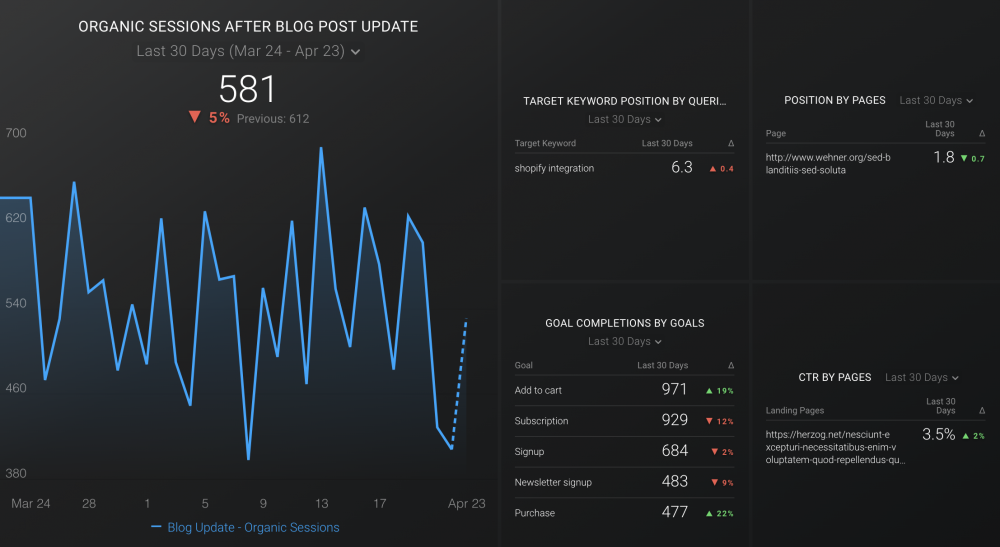
Find great topics.
Use the Console to spot upcoming trends. You can use the Search Results performance report and filter down to the most recent dates to find out where new organic search traffic is landing.
Additionally, you can look at CTR, impressions, and average ranking to forecast where traffic will soon go.
These details will allow you to audit your page’s keyword targeting, evaluate the copy, improve navigation, and boost your link building to take advantage of a new and trending landing page.
Identify what questions people have on a service that you offer, and use those queries to improve content through FAQs, CTAs, and others.
Here are a few steps you can follow.
- Open the Performance report.
- Go to the Pages tab.
- Sort by Impressions (high to low) and see which pages show up the most in SERPs.
- Click on one of your vital pages.
- When the report reloads, click Queries.
- Edit the date and click Compare, then Compare the last three months against the previous period.
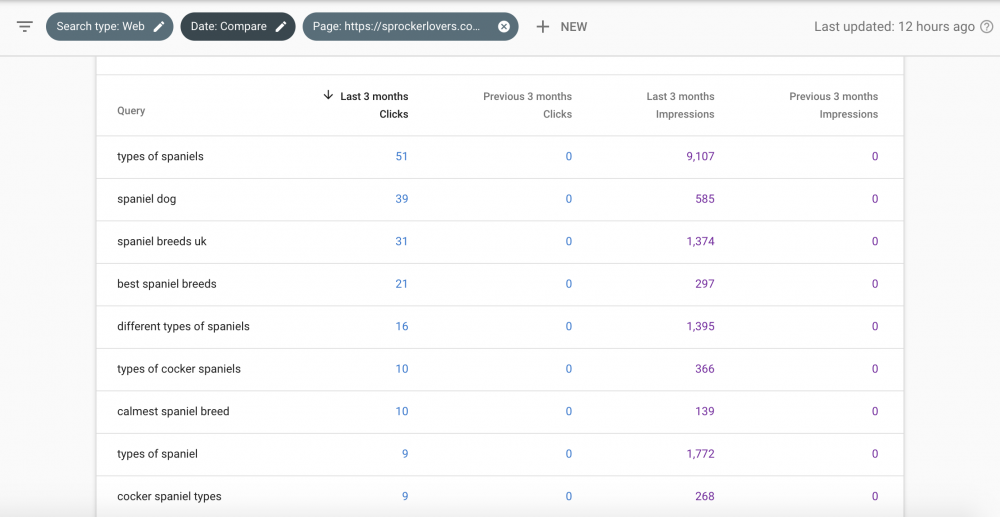
The key is finding Queries that show-up high on the Impressions list for the past three months, but did not generate as many impressions in the three previous months. Find those that may indicate that the page is ranking for new Queries, or that these new ones are gaining search volume, and would represent new traffic opportunities.
It is better if you export the data to a spreadsheet and calculate the change. Then, sort by change value. With that, you will see the most prominent movers (up or down) over time.
Mix this insight with your number of clicks to see if the increased Impressions are turning into more clicks/traffic. This is an indication if your ranking is gaining or maintaining, or if Impressions increased, but Clicks did not, the positions could be falling.
See how your data compares to competitors.
Always keep in mind to compare your results against your competitors’.
See which tactics they are using If they are ranking above you in searches. Look at what they do that you don’t.
Benchmark on their SEO and do 100% better.
Look into your CRO, Cx, and CJO.
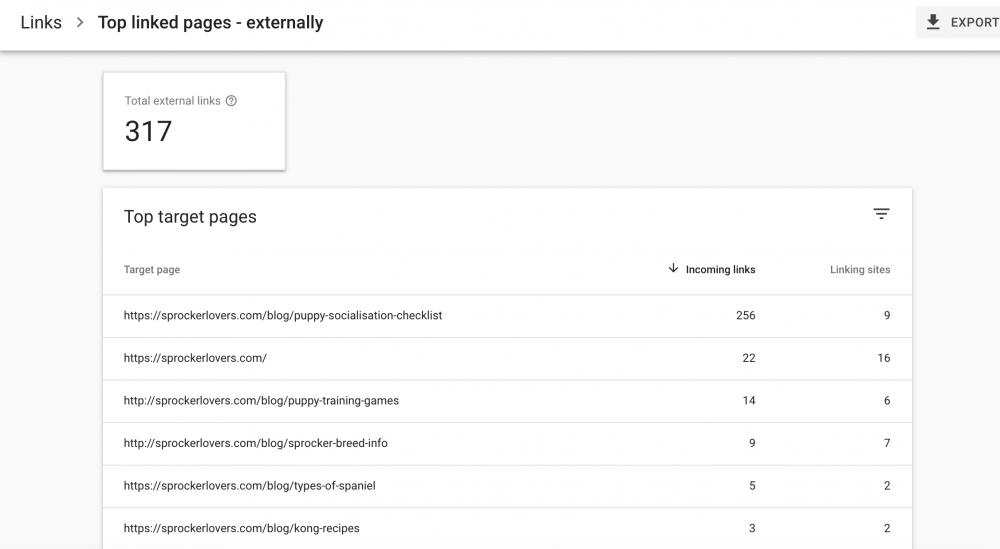
Monitor your most popular backlinks.
In terms of position on SERPs, you can use backlink tools to examine what sites are linking to you and how much traffic they are bringing in.
Compile the data in a spreadsheet, not just including the total number of links, but also the domains where the links are coming from.
After which, you must search for sites that are similar to those already linking to yours.
Find out their SERP position and if they’re indexed and see if you can provide a guest post for their blog or any content for their resources page.
See site links.
Use Google Search Console to find site links that Google thinks are relevant to the main query.
They are excellent additions to your result in SERPs as they give your visitors more options to visit more in-depth pages without having to navigate through your homepage. If you can’t find any site links, continue adding relevant content. Do this until your site gets a critical mass for Google’s algorithm to pick up.
Seek out internal linking opportunities.
Find pages that need internal linking. Click more under the top linked pages and then select internal links.
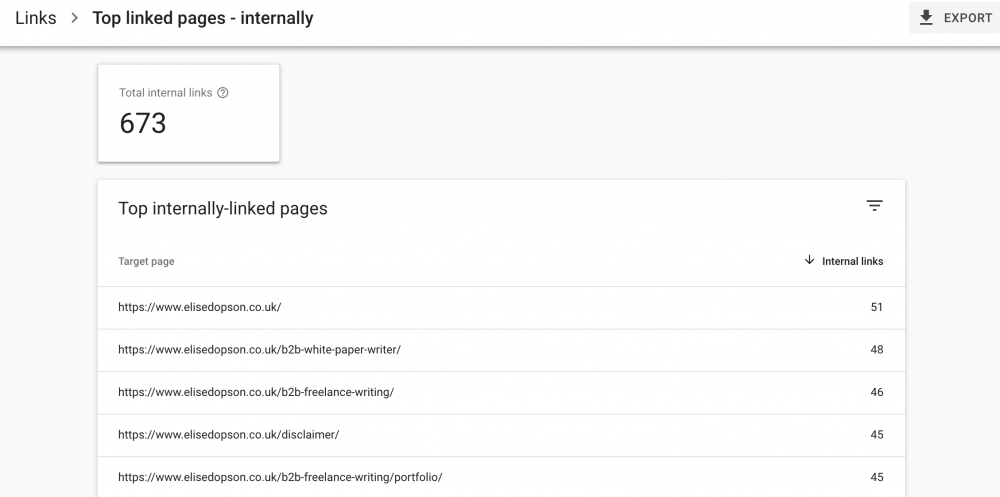
Internal linking can help your new page get indexed quicker. Internal links will transfer PageRank to the new page, which could help increase its ranking.
Monitor the SEO performance of a new website.
A new website might get almost no traffic yet. However, you can still track the progress of your website by checking impressions in Google Search Console.
If the impressions continuously increase, this means that more keywords are showing up in the SERPs. This implies clicks and traffic coming their way.
When impressions are flattened out, and you have almost no traffic, it means that you have to do another thing to kick start your site.
Measure your search performance.
Look at your performance over time.
It is smart to monitor the average position of your website in the SERPs monthly. This information will indicate whether your SEO efforts are working or not.
If your average position increases, it means that your efforts are not in vain. However, if the average position decreases, then you must reevaluate your SEO strategies.
You can also check the last seven days of each landing page to see if the number of clicks and impressions rise. With this, you will have an accurate average of your position on that timeframe.
Remember to use the date comparison for queries. A keyword might have excellent CTR, but a higher CTR from a prior month indicates there’s some work to do.
The performance report will give you an excellent indication of your website’s health and where you can start when improvements have to be made.
You can also compare yearly or quarterly performances.
You can gather quite a few insights from this, including checking rankings and positions now compared to before and clicks and impressions. It also gives you a good idea of your click-through rate.
Even if you have much better rankings and stronger impressions but a low CTR now, then you need to fix your CTA’s or your meta title/descriptions, and you should look into what you are doing on other channels so you can capitalize on missed opportunities.
Check which keywords and pages get high numbers of impressions but low amounts of clicks and then work on your SEO to increase the rank for the pages/keywords.
This will leave the third column for you that shows you the “difference.” Toggle this to see the pages that have gained the most number of visitors and which ones have lost the most.
This tells you what works and what does not and what pages have the most significant changes in the SERPs.
Be aware of your audience because how they use your site will create a domino effect that impacts your strategy directly. See how and why visitors are on your website, where and when they leave, and how to answer their queries and close funnels.
Collaborate with your team.
Most companies have only one person managing their SEO. However, experts advise that this should not be the case as it would be hard to explain movements to people who are not empowered.
A professional marketer says that you must carefully look over your search query report at the end of each month collaboratively, and you should watch out for what queries are getting a high number of impressions but few clicks.
High-volume, low CTR searches propose that while you have a page that ranks for search words, it is irrelevant. Hence, there is a need to write a highly-focused page for those queries, which will be easier made when everyone is on board.
You should use the Search Console to make sure that the correct page is ranking.
Do not forget that Search Console data isn’t perfect.
One of the best ways to maximize the use of Google Search Console is to display the data using another tool like Data Studio.
Experts agree that you should not use the overall average position as a KPI.
When Google measures the average keyword position, it looks at the top 1000 places in the SERPs. This implies that if you gain new keywords, but rank low, your overall average position will decrease.
You can consider the average position as KPI if you do it keyword-by-keyword. Even then, experts argue that it is not a highly vital metric when you think of the discrepancy in click-through percentage between keywords.
What you should pay attention to is what your organic click drivers are. For most websites, it is commonly the first thirty queries in the Console. You must optimize for pages that are ranking for those queries.
One red flag is extremely high impression counts. Try to filter by impressions and see which pages are being viewed but are unclicked. Maybe their content is irrelevant, or the SERP listing is not outstanding. Both issues are SEO problems, and you should triage them at once.
Another expert tip for using the tools is that you must understand its limitations and avoid expecting it to do what it cannot. GSC is perfect for regularly tracking positions that your website was found on SERPs by keyword.
One key is to understand user engagements on SERPs with the website. The tool is particularly unhelpful when it comes to an understanding of what users do after leaving the SERP.
More in-detail and in-depth tracking is needed for a deeper study of user engagement. GSC is perfect for search rankings, and it is a highly accurate tool, whether your version is free or paid.
Seek out internal linking opportunities to increase rankings.
Consistently take advantage of Google Search Console for internal link building. You’ll see almost automatic results when you link from pages with authority to pages that you want to push up in rankings.
This tactic is excellent in getting your site onto page one of Google.
Look for pages ranking in 4th and 9th positions, and look for high-authority pages on your website by sorting pages by impressions and clicks. What you’ll find are generally the most well-regarded pages in Google’s perspective.
After having identified your high-authority and underperforming pages, link the high-authority pages to the underperforming pages. When you do this, some authority from the high-authority pages is shared with underperforming pages. This gives your underperforming pages a boost in the rankings.
Find out what pages are wasting your budget.
Google doesn’t always crawl each of your pages. Sometimes, it has a crawl budget that limits the number of pages it regularly crawls.
This is a potentially vital issue as it could lead Google’s crawlers to ignore your new or updated content.
For small websites, a crawl budget usually doesn’t pose a problem. However, pages with thousands of pages and content can have a disadvantage. When you have a significant amount of low-value URLs, they can negatively affect crawling and indexing for your website.
Use Google Search Console to find low-value pages that can negatively affect your crawl budget. The tool is useful in finding pages that nobody visits anymore.
Look for the pages that get the lowest number of impressions and clicks. You can opt to delete them, 301 redirect them to pages of similar content or update its contents.
Studies show that when you delete pages with little or no traffic or 301 redirect them to significantly better content, Google will add more value to relevant pages more. This method highly increases the traffic on your website.
Identify the ideal target keywords.
When you already have plenty of content, you probably should review your existing pages and find out if there are potentials to improve rankings on specific keywords. It is common to make some mistakes when picking the perfect keywords the first time.
You have to get the ideal keyword for any content you’ve published and then improve and reoptimize the page with its perfect keyword. To do this, you have to find out what queries your page ranks for with impressions, its click-through rate, and the average position data.
Sort by impressions and find what query has the most impressions that rank in positions 3-7. Add this query to the SEO title or H1 on your page.
Experts say that these simple tweaks to page metadata and content can take you from page two to one. Within two weeks of implementing the changes, you will probably get the traffic you are looking for.
Seek out opportunities to better your CTR.
Click-through-rate is a highly crucial ranking factor. When your result has little or no clicks, you will fall off the ranks as Google will perceive your result as irrelevant. However, if your result has many clicks, your rankings will go up.
Focus on your CTR on queries and pages that you are already ranking for. If you have impressions but have no click-throughs to your page or article, all you need to do is spend a few minutes finding out how to optimize your title, meta, or URL to attract people to click to your content.
Monitor the other pages that are ranking around you and ask yourself some critical questions.
- Does the page’s content match search intent?
- Does the title represent the quality of the content?
- Are other content better than mine?”
- Am I anticipating and answering the questions of my readers?
You have to craft attractive title tags that intrigue readers. Include numbers and parentheses so that it is appealing to a broader audience.
Also, you must ensure that the meta-description speaks of why readers must click on your content instead of others’.
Look for pages that require additional optimization.
The tool is the most excellent source of data when it comes to rankings of pages. Whether you get the information indirectly from reports fed into Google Analytics or directly from GSC, you will have excellent insights for your SEO.
Find a page that ranks and look at how high it ranks for what phrases and improve its optimization so that it ranks better for that phrase. This is one of the fastest ways to improve search traffic.
Find keywords that rank on page two or the low end of page one. Keywords that have excellent impressions but have lower ranks are essential keywords that need your attention. They can potentially generate excellent traffic.
Use Analytics to see what pages drive the most traffic and use Console to find data that you can use to optimize the pages even more.
Find out what terms every page ranks for that are in 2nd to 10th positions in search results. Focus on those items. As long as they’re relevant, you can take those terms and turn them into the copy on that page.
This is an excellent optimization method for historical blog posts that can be pulling in some organic traffic but are performing low, given the high quality of the content.
Search for keywords to target in paid campaigns.
The tool is an incredible source of keyword ideas and ad copy suggestions. It is also a goldmine for the best landing pages for your Google Ads.
Set up your performance report to display clicks and impressions for all queries with the timeframe “Last three months.” After which, sort by impressions, and you’ll find keyword ideas for your ad campaign.
Select ‘Average CTR’ and ‘Average position’ and then sort by position to view what search terms your pages rank most significantly for. Use this landing page and keyword combo for a higher chance of raising the quality score for your ad group.
When you have a higher quality score, it means you have a lower cost-per-click and a more top position.
Get new content ideas.
You can export up to 1,000 of the queries that you show up for in search. Export this data and categorize queries by topic or category to have an understanding of the groupings of keywords that your site shows up for.
The data will show what areas you need to spend more time on so that you can get more impressions or clicks in organic search. Also, you’ll have ideas for topics you can write articles about that will help increase your traffic and improve click-through rates.
- Measure the changes in both branded & non-branded search volumes.
Google Search Console has an expanded keyword database. Its vast data is one of its most-used features.
The tool reaches deep back in further history, which is useful for tracking and assessing year-over-year keyword performance, whether branded and non-branded. This results in a more accurate dataset.
Decrease the bounce rate by seeking out negative keywords.
With Console, you can find out what keywords your site ranks for so that you can identify negative keywords.
Negative keywords are queries you are ranking for but have misplaced intent. Inappropriate keywords will have a negative impact as it affects your bounce rate.
You can decrease your bounce rate by fixing the problem with appropriate corrective measures.
One way is to update your content to more accurately address the keywords you’re ranking for but did not cover in your content.
Another is to create new content that addresses the intent of a negative keyword and linking it to the existing post.
Give Google additional information without adding structured data.
Add structured data to your site so that you give Google more information regarding your content.
You can use structured data to give detail on whether a piece of content is an article, a FAQs list, recipe, or review.
Structured data assists Google in understanding your content better, and it can result in expanded search result listings.
As an example, this is a search result that has structured data for both a recipe and ratings. Both of the pieces of data results in a more detailed search result:

Keep in mind that not every SEO is experienced in the area of web development. Frequently even code-proficient SEOs just don’t have access to essential website code.
Using the data highlighter in Console, you can personalize how a site will display on search result pages. This enables pages to stand out, improve rankings, and contain more context to give Google information about your content.
The data highlighter makes it convenient to tag different content on a website without the addition of structured data to the code. All you have to do is pick the item you’ll be highlighting, whether it be reviews, software, or restaurants. Then, enter the URL of your page, and begin highlighting.
After you highlight a piece of content, you can continue in specifying more information about it, whether it’s an official URL, a picture, or a download URL.
Google ranks items depending on contextual cues. Using the data highlighter is efficient in improving the context of your website content.
Use other tools alongside GSC.
When you continually optimize your site for search, you’ll find out the time and again that you’ll need more data to do an excellent job consistently.
You’ll need essential data fromGoogle Analytics and Google Search Console even when you are only doing basic SEO.
As you advance and improve in the practice, it would be helpful to use data from other popular SEO tools like SEMrush, AccuRanker, Moz, and Ahrefs.
One way to consolidate this data is to connect Google Search Console with Google Analytics. When you combine these tools, you are granted access to keywords and search performance data in a way that eliminates the need to switch back and forth between each of them.
Databox is another option. It is a data visualization tool that enables you to create shareable dashboards that centralize information from 70+ tools, including Analytics, Console, Ahrefs, SEMrush, AccuRanker, and Moz.
10 Advantages of Using Google Search Console
- It measures your keyword topic cluster performance and tells you how well your content themes are doing.
- It is excellent in finding unicorn content (content with CTRs of more than 10% + rankings on pages 1 or 2).
- It can point out pages that are missing from your website.
- It identifies the most valuable branded and non-branded keywords for you.
- It finds pages with strong impressions, low CTRs, and that are ranking on the 1st page so you can improve it.
- It can find pages with strong impressions and low CTRs that rank on the 2nd page so you can generate additional content topics to increase your authority on the subject.
- It drills down into queries for individual landing pages so that it can discover new or irrelevant keywords your page ranks for.
- It goes deep down into queries for particular landing pages and discovers new ad group keywords and themes.
- It is easy to use.
- You can use it for free.