If you have issues with aspects of your technical SEO, no matter how valuable your site content is, it’s likely you will struggle to rank highly in the search engines.
As a result, it’s really important that you spend some time optimising the technical SEO of your website.
Fortunately, regardless of your technical knowledge, experience and skills, you can easily perform a periodic technical SEO check on your website.
In this article, I will share 10 critical technical SEO elements you need to check, as well as easy-to-implement tips to improve your website’s organic ranking.
The Top 10 Technical SEO Elements
1. HTTP Status Codes
HTTP status codes are server responses to browsers. When a user visits a website, the browser sends a request to the server on which the site is hosted. Then, the server responds with a code, such as 302, 301 and 404, for example.
Each code means something different: “300” errors typically means redirects and “400” errors typically means errors.
It’s important for website owners to recognise where and why HTTP status codes occur in order to fix them, as they can have a serious negative impact on SEO.
The best way to find and fix them is to use a tool such as Oncrawl.com or Google Search Console.
While logged into your Oncrawl account, select the “Indexability” option in the left-hand panel and select the “status codes” option to see the different status codes that appear and which pages they appear on.
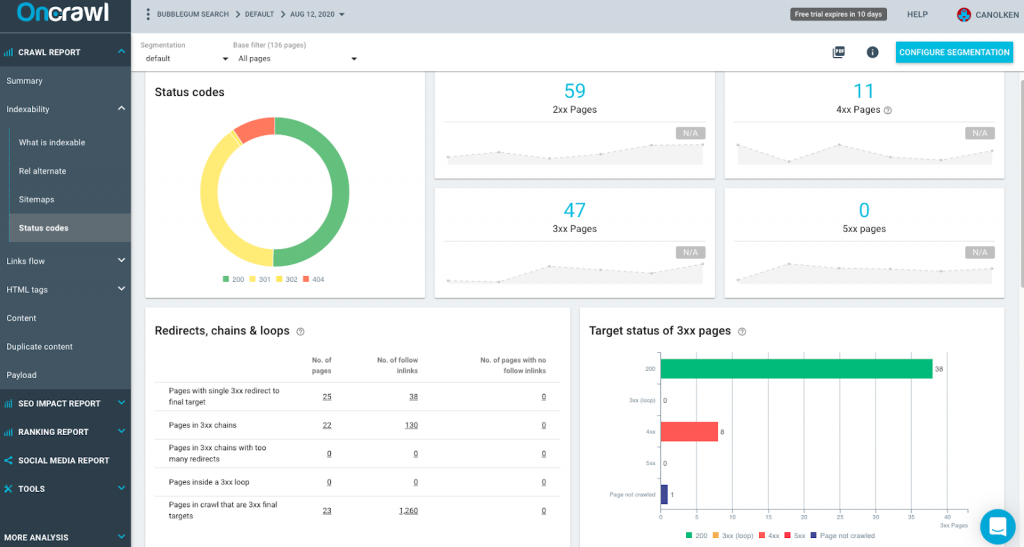
Here’s a list of the most common status code classes and what they mean for your website:
- HTTP Status Code 200: This is the perfect code for a page. It means the page is functioning correctly. You may want to quickly check that you haven’t got any pages indexable that shouldn’t be — in which case, consider applying a noindex or canonical tag or 301 redirecting to an equivalent page.
- HTTP Status Code 301: This means a URL has been permanently redirected to another page. All visitors and bots that land on the page are automatically sent to the new page, along with any link equity.
- HTTP Status Code 302: Similar to a 301 redirect, however, a 302 is a temporary redirect. If you see this code, consider whether a 301 would be better to use.
- HTTP Status Code 404: This means a page cannot be found by a user or a bot. You need to map out and redirect the page to the most relevant & equivalent page.
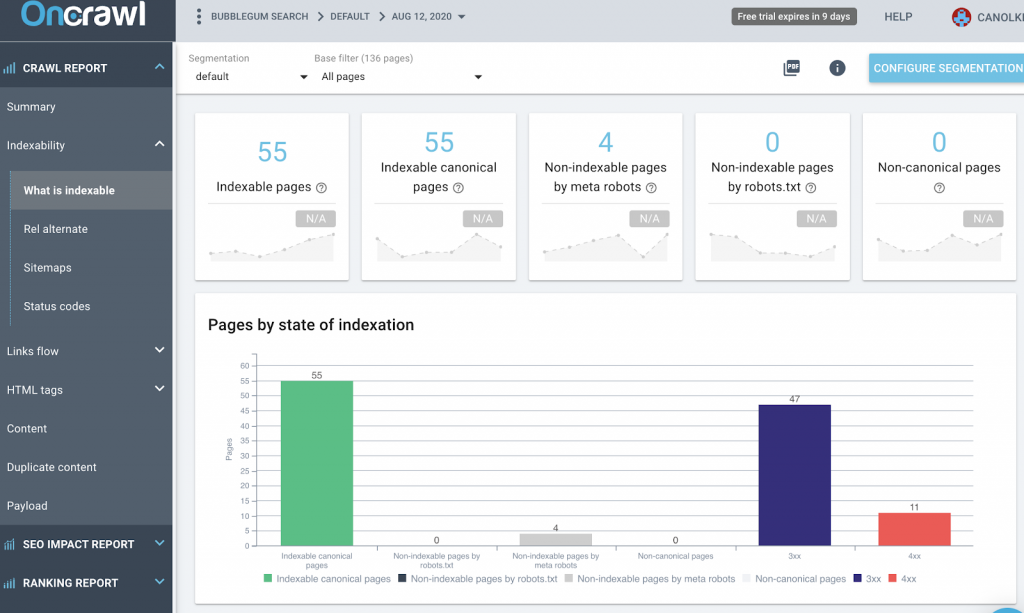
2. Indexation
It is important that you understand whether search engines are able to crawl and index your website effectively (this is a big topic, if you’re a newbie to technical SEO, we highly recommend reading this article by Moz).
In order to drive organic traffic, your content needs to be easily crawled by the google bots to ensure that it can be indexed.
Tools like Oncrawl give you a clear picture of what Google sees, for example, the pages the bots frequently crawl, any newly crawled pages and even any errors or redirects that are negatively impacting your Google crawl budget.
This allows you to ensure your highest priority pages are reachable and optimised correctly to achieve the best rankings, as well as giving you a clear understanding of how your website architecture distributes your content.
3. XML Sitemaps
In simple terms, an XML sitemap is a list of all the URLs associated with a website.
It provides a roadmap for search engines to tell them what content is available and how to reach it.
Why is it important to check your sitemap is set up correctly?
If you waste your Google crawl budget on pages that aren’t important or you don’t include important URLs, it’s likely the correct pages will not rank highly in the search engines.
Therefore, it’s important to check your sitemap on a regular basis to prevent incorrect URLs from being crawled and indexed, as well as ensuring that important URLs are not excluded.
Here are two important checks when reviewing your sitemap:
- Check that only the main or important URLs are included.
- Ensure that only indexable URLs are included in your sitemap. Try to eliminate error code, canonicalized, no indexed or orphaned URLs. In other words, the sitemap should include only pages that serve a 200 response code.
4. Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are just what they sound like: pages that exist on a website but aren’t linked to any “parent” page. This means that users can’t find them by navigating your website or clicking on other pages to link to them.
However, orphan pages have a negative impact on SEO. As there aren’t any internal links, link authority is not passed to the pages and there is no semantic or structural context for search engines to evaluate the pages.
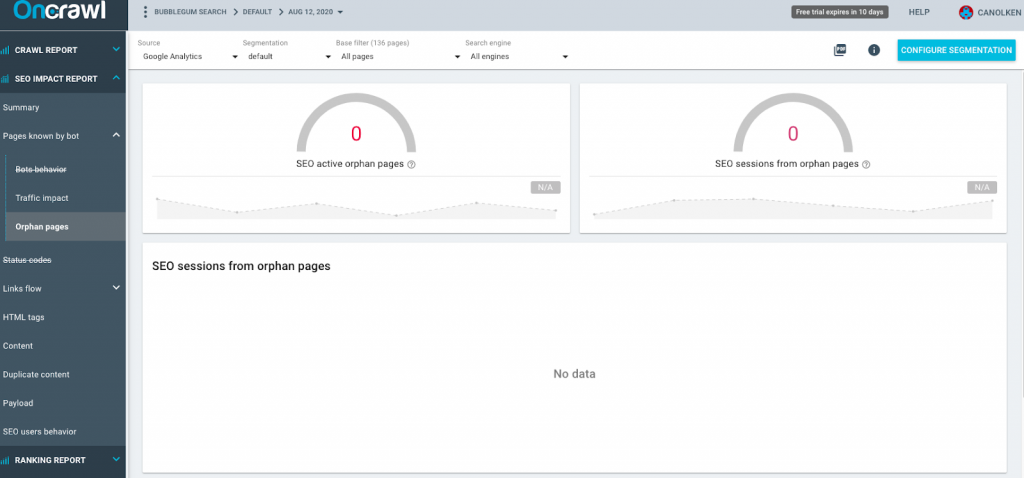
The best way to see if your website contains any orphan pages is to use a tool, such as Oncrawl to help you find and fix them.
As you can see from the example below, Bubblegum doesn’t have any orphan pages (hooray!).
However, you can check your website by logging into Oncrawl and selecting the “Orphan pages” option under the “Pages known by bot” tab on the left-hand panel.
Armed with your list of orphan pages, next you need to decide how to fix them. This will depend on why they have been orphaned, what the page is used for and how much traffic they generate.
- Irrelevant, unnecessary or thin content pages can be deindexed.
- Relevant pages should be re-incorporated into the website architecture and linked to from relevant pages or sections.
- Pages that receive inbound links from other websites or have a new page equivalent can be 301 redirected.
5. Page Speed
Page speed refers to the amount of time it takes for a website page to load. Page speed also refers to “page load time” or how long it takes for a browser to display page content.
Ultimately, the more content on a page, such as text, images, or video, the longer it typically takes for that page to load.
Although it may seem insignificant, page speed can have an impact on not only SEO (albeit small) and search rankings but even conversion rates and revenue.
Even a page speed decrease by a few seconds can have a massive impact.
In fact, a decrease in page speed from one second to three seconds can increase bounce rates by up to 32 percent.
Fortunately, there are tons of tools, like Google’s PageSpeed Insights that quickly analyse your website’s speed, as well as offering recommendations to fix any issues.
6. Canonical Tags
A canonical tag, tells search engines that a specific URL is the “master” page.
Canonical tags essentially help to control instances of duplicate content, which is something that should always be avoided.
You may think you are safe from the perils of duplicate content, however, it’s easier than you think to mistakenly add duplication on your website.
For instance, your home page may feel like just one page to you, however, to Google each of these is a different page:
- http://www.example.com
- https://www.example.com
- http://example.com
- http://example.com/index.php
Using canonical tags helps to control duplicate content by telling the search engines that a specific URL represents the master copy of a page.
7. Duplicate Content
When search engines crawl websites, they look for duplicate content or content that is too similar to other pages on your website.
Duplicate content causes issues for bots as it makes it harder for them to determine which page is the most relevant for a given query.
Tools like Oncrawl allow you to find duplicate pages or near-duplicate pages. You can also see if your canonical strategy is managing your duplicate content or if there are issues.
There are a handful of best practices to follow when it comes to eliminating duplicate content issues. The majority of problems can be fixed by canonicalisation using 301 redirects, rel=canonical or parameter handling tools in Google Webmaster Central.

8. Keyword Usage and Presence
The success of any website SEO strategy should involve the usage and presence of keywords in your content. For example, this means adding keywords where necessary (and naturally) in your introductions, conclusions and ideally H1, H2, headers.
If you are unsure of what keywords you want to use in your content, or what keywords you want to rank for, you can use a paid keyword search tool, or a free tool such as Keyword.io or ubersuggest to get you started.
Then, once you have a list of keywords and phrases to use in your content, the next step is to add them to your blog and website.
One important note to consider keyword stuffing. Your keywords must appear naturally in your content.
[Ebook] Technical SEO for non-technical thinkers
9. URL Structure
Your page URLs play a super important role in SEO.
URL structures that are clean and easy to read and understand help both search engines and humans to see what a page is about before even clicking on it.
Keep URL structures short, sweet, clean and incorporate relevant keywords in them, if possible.
Here are a couple of examples to give you an idea:
❌ http://www.domain.com/top/click=6EE2BF1AF6A3D70
✅ www.domain.com/womens/top
10. Optimise for Mobile
The majority of website traffic today occurs from a mobile device.
In fact, according to Statista, mobile accounts for approximately half of all web traffic worldwide, at 51 percent of global website traffic.
As well as driving the majority of traffic, mobile is now responsible for 40% of ecommerce sales.
It’s hardly surprising that Google has moved to a mobile-first index as well. The mobile content of your website determines how well your website ranks in the search engines.
In other words, your website should be optimised for mobile devices as this not only provides a better user experience but also will help boost your SEO rankings.
Luckily, there are loads of tools that will quickly analyse your website’s mobile-friendliness and offer recommendations for improvements.
For instance, Google Search Console checks all of the pages on your website to ensure that they are responsive, quick to load and that all elements fit on the page and fonts are legible on mobile screen sizes.
To find out recommendations from the search console, simply login and navigate to Mobile Usability from the left-hand menu.
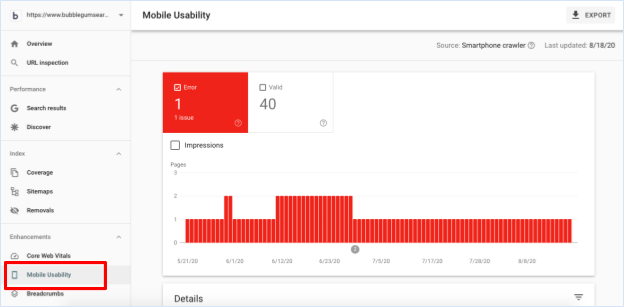
Scroll down the page to find a list of suggestions like this:

Mobile SEO is a huge topic on its own. But I have also written this guide: Mobile SEO Audit in 10 Easy Steps to help kick start your own mobile SEO.
Boost Your SEO Strategy with the Right Tools
Technical SEO may be the less glamorous cousin of content SEO and link building/ Off Page SEO.
However, if you’re serious about ranking highly in the search engines, it’s of equal importance.
To sum up, here is a 10-part checklist of must-do tasks to check and optimise your website’s technical SEO:
- HTTP Status Codes
- Indexation
- XML Sitemaps
- Orphan Pages
- Page Speed
- Canonical Tags
- Duplicate Content
- Keyword Usage and Presence
- URL Structure
- Optimise for Mobile
Which technical SEO task are you going to fix first? Let us know in the comments section below.