Do you know what’s happening on your website every day? The first thing that comes to mind when answering this question would most likely be to use audience and behavior tracking tools.
There are many such tools available on the market including: Google Analytics, At Internet, Matomo, Fathom Analytics, Simple Analytics to name just a few. While these tools do allow us to have a pretty good overview of what’s happening at any given time on our websites, the ethical practices employed by these tools, more specifically Google Analytics, are once again being called into question.
This suggests that there are other sources of data that currently are not being sufficiently exploited by all website owners: logs.
Analysis tools and GDPR (focus on Google Analytics)
Personal data has become a sensitive subject in France since the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the creation of the National Commission on Informatics and Liberty (CNIL). Data protection has become a priority.
So, is your website currently still “GDPR friendly”?
If we take a look at all websites, we can find that many have found a way to get around the rules by using their cookies (data collection banners) to gather the information they need while others still strictly adhere to the official regulations.
By collecting this information, data analysis tools allow us to analyze where the audience comes from and visitor behavior. This kind of analysis requires an impeccable tagging plan to collect the most reliable and accurate data possible and ultimately the data collected is the result of each action and event on a site.
Following a number of complaints, the CNIL decided to put Google Analytics on notice by making it illegal in France, for the time being. This sanction comes from the apparent lack of supervision regarding the transfer of personal data to the intelligence services in the United States although visitor information had been collected with consent. Developments should be monitored closely.
In this current context, with limited or no access to Google Analytics, it could be interesting to look at other data collection options. A compilation of a site’s historical events and relatively simple to recover, log files are a great source of information.
Despite log files providing access to an interesting archive of information to analyze, they don’t allow us to display business values or a site visitor’s real behavior, such as site navigation from start until the time he or she validates a shopping cart or leaves the site. The behavioral aspect remains specific to the tools mentioned above, however; log analysis can help us to get pretty far.
Understanding log files
What are log files? Logs are a type of file whose main mission is to store a history of events.
What kind of events are we talking about? Essentially, ‘events’ are the visitors and robots that access your site every day.
The Google Search Console can also collect this information, but for several reasons – in particular, privacy reasons – it applies a very specific filter.
(Source : https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/7576553. “Differences between the Search Console and other tools”.)
Consequently, you will only have a sample of what a log analysis can provide. With the log files, you have access to 100% of the data!
Analyzing the lines of log files can help you to prioritize your future actions.
Here are some examples of past visits to the Oncrawl site from different robots:
FACEBOOK :
66.220.149.10 www.oncrawl.com - [07/Feb/2022:00:18:35 +0000] "GET /feed/ HTTP/1.0" 200 298008 "-" "facebookexternalhit/1.1 (+http://www.facebook.com/externalhit_uatext.php)"
SEMRUSH :
185.191.171.20 fr.oncrawl.com - [13/Feb/2022:00:18:27 +0000] "GET /infographie/mises-jour-2017-algorithme-google/ HTTP/1.0" 200 50441 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; SemrushBot/7~bl; +http://www.semrush.com/bot.html)"
BING :
207.46.13.188 www.oncrawl.com - [22/Jan/2022:00:18:40 +0000] "GET /wp-content/uploads/2018/04/url-detail-word-count.png HTTP/1.0" 200 156829 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; bingbot/2.0; +http://www.bing.com/bingbot.htm)"
GOOGLE BOT:
66.249.64.6 www.oncrawl.com - [21/Jan/2022:00:19:12 +0000] "GET /product-updates/introducing-search-console-integration-skyrocket-organic-search/ HTTP/1.0" 200 73497 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0.1; Nexus 5X Build/MMB29P) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/97.0.4692.71 Mobile Safari/537.36 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)"
Please note that some bot visits may be fake. It’s important to remember to verify the IP addresses to know if they are real visits from Googlebot, Bingbot etc. Behind these fake user agents, there may be professionals who sometimes launch robots to access your site and check your prices, your content, or other information they find useful. In order to recognize them, only the IP will be helpful!
Here are some examples of Oncrawl site visits by Internet users:
From Google.com:
41.73.11x.xxx fr.oncrawl.com - [13/Feb/2022:00:25:29 +0000] "GET /seo-technique/predire-trafic-seo-prophet-python/ HTTP/1.0" 200 57768 "https://www.google.com/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 10; Orange Sanza touch) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/97.0.4692.98 Mobile Safari/537.36”
From Google Ads utms:
199.223.xxx.x www.oncrawl.com - [11/Feb/2022:15:18:30 +0000] "GET /?utm_source=sea&utm_medium=google-ads&utm_campaign=brand&gclid=EAIaIQobChMIhJ3Aofn39QIVgoyGCh332QYYEAAYASAAEgLrCvD_BwE HTTP/1.0" 200 50423 "https://www.google.com/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/96.0.4664.110 Safari/537.36"
From LinkedIn thanks to the referer:
181.23.1xx.xxx www.oncrawl.com - [14/Feb/2022:03:54:14 +0000] "GET /wp-content/uploads/2021/07/The-SUPER-SEO-Game-Building-an-NLP-pipeline-with-BigQuery-and-Data-Studio.pdf HTTP/1.0" 200 3319668 "https://www.linkedin.com/"
Why analyze log content?
Now that we know what the logs actually contain, what can we do with it? The answer: analyze them, like any other analytics tool.
Bots or robots
Here, we can ask ourselves the following question:
Which robots spend the most time on my website?
If we focus on search engines, with a detailed view of each bot, here is what we can see:
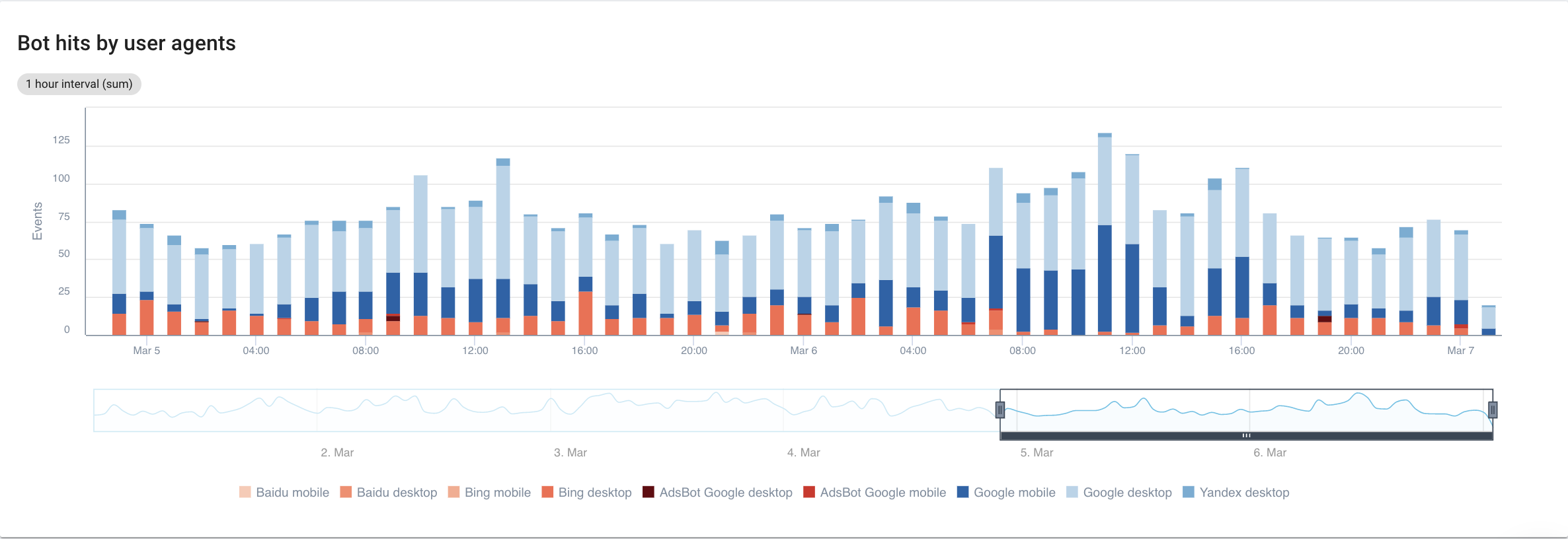
Source: Oncrawl application
Clearly, Google Mobile and Desktop spend a lot more time crawling than Bing or Yandex bots. Googlebot has a global market share of over 90%.
If Google crawls my pages, are they automatically indexed? No, not necessarily.
If we go back a few years, Google employed an automatic reflex to index pages directly after visiting them. Today, this is no longer the case given the volume of pages it has to process. As a result, an SEO battle ensues in regards to the crawl budget.
All that being said, you may ask: what’s the point of knowing which bot spends more time than another on my site?
The answer to that question all depends on each of the bots’ algorithms. They’re each a little different and don’t necessarily return for the same reasons.
Each search engine has its own crawl budget which it divides among these bots. In other words, that means that Google divides its crawl budget amongst all of these bots. Therefore, it becomes quite interesting to look a little closer at what GooglebotAds does, especially if we have 404s lying around. Cleaning them up is a way to optimize crawl budget and ultimately your SEO.
Cross-referencing GoogleBot data with Oncrawl Crawler data
In order to go deeper into analyzing GoogleBot’s behavior, Oncrawl cross-references log data with crawl data to get the most detailed, accurate information.
The goal is also to affirm or refute the hypotheses linked to several KPIs such as depth, content, performance, etc.
Accordingly, you have to ask yourself the right questions:
- Does GoogleBot crawl all pages on your site?Take an interest in the crawl ratio which clearly provides this information that you can also filter with a segmentation of your pages.
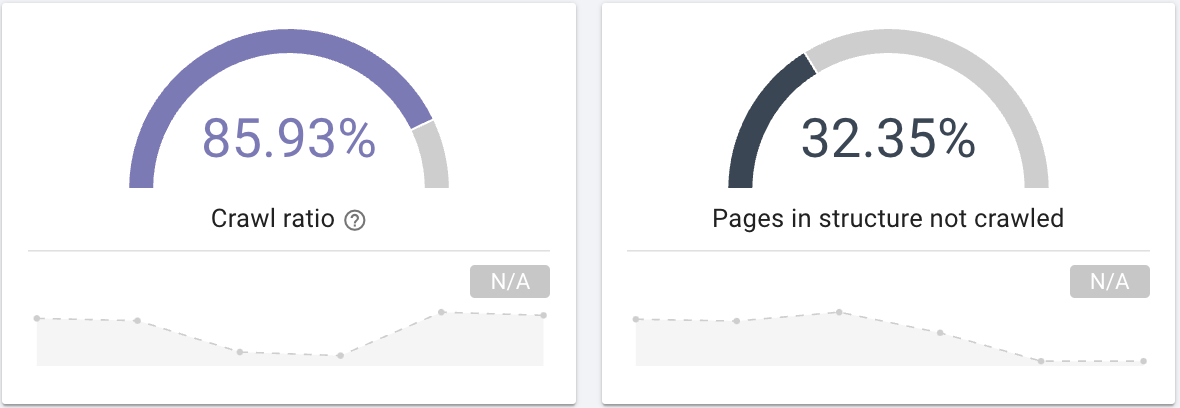 Source: Oncrawl application
Source: Oncrawl application
- On which category does GoogleBot spend its time? Is this an optimal use of the crawl budget?
This graph in Oncrawl’s SEO Impact Report cross-references the data and gives you the information.
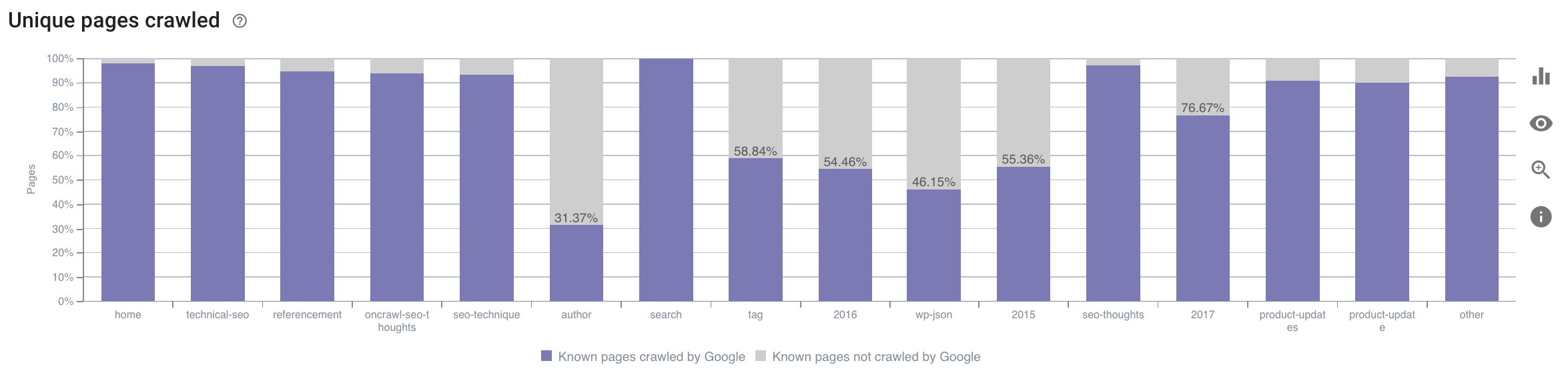
Source: Oncrawl application
- We may also have questions outside the realm of what the Oncrawl crawl report offers by default. For example, does the length of the description have an impact on the Googlebot’s behavior? We have the data on this thanks to the crawl, so we can use it to create a segmentation just as below:
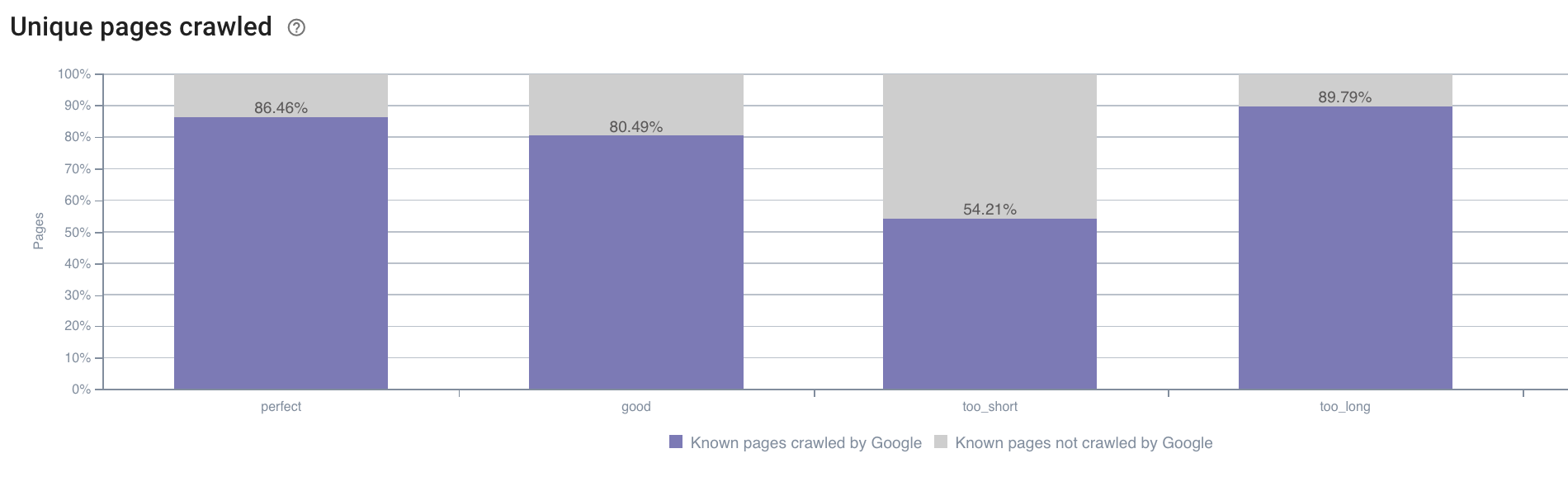
Source: Oncrawl application
Descriptions that are too short are crawled much less than those that have the ideal size designated as “perfect” or “good” here by the Oncrawl application (between 110 and 169 characters).
If the description meets the criteria of relevance and size, among others, Googlebot will happily increase its crawl budget on relevant pages.
Note: pages which are deemed too long are sometimes rewritten by Google.
Analyze website visits using logs
Next, if we look at the example of SEO, since this is what we are trying to analyze with Oncrawl, I suggest you ask yourself another question:
- What is the correlation between Googlebot’s behavior and SEO visits?
Oncrawl has the same graphs to cross-reference the data between that of the crawl and the SEO visits retrieved in the logs.
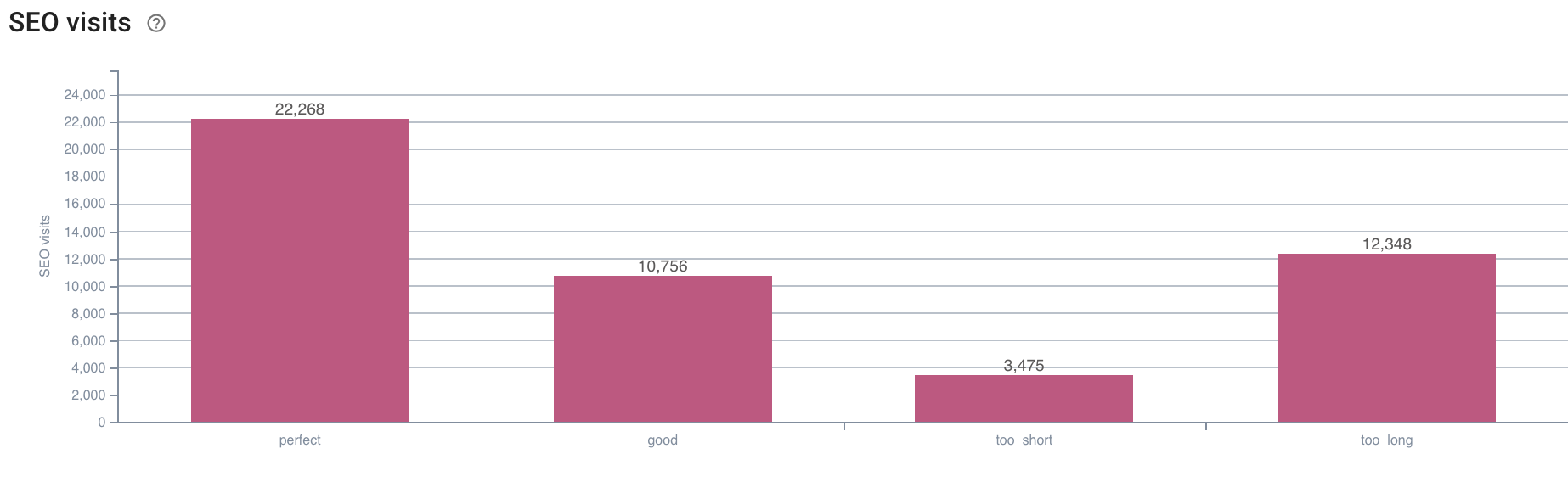
Source: Oncrawl application
The answer is very clear: the pages that have a “perfect” description length are the ones that seem to generate the most SEO visits. We must therefore concentrate our efforts on this axis. In addition to “feeding” Googlebot, users seem to appreciate the relevance of the description.
The Oncrawl app provides similar data for many other KPIs. Feel free to verify your hypotheses!
In conclusion
Now that you know and understand the possibility of exploring what happens on your site every day thanks to the logs, I encourage you to analyze the internet users and robot visits in order to find various ways to optimize your site. The answers may be technical or content-related, but remember that good segmentation is the key to good analysis.
This kind of analysis is not possible with Google Analytics tools, but their data can sometimes be confused with that of our crawler. Having as much data as possible at your disposal is also a good solution.
To get even more out of your log data and crawl analyses, feel free to take a look at a study conducted by the Oncrawl team that compiles 5 SEO KPIs related to logs on e-commerce sites.

